Using the XML Data Wizard
Select any matching type or element from the drop-down list to create a XML data file for the root element. For a complex type or element, you can generate an XML data file. If the Generate button is greyed out, the variable selected is not of a compatible type. For any variable, use this editor to type in appropriate literal values.
For details on the Preferences page, see below.
Overview
The XML Data Wizard automatically generates the following types of data:
- • Sample data file for a WSDL message that is a complex type
Open the XML Data Wizard as described in Generating a Sample Data File
- • Literal contents of a complex variable in the From side of a copy operation
Open the XML Data Wizard as described in Copy Operation Literal Contents Examples.
- •Literal contents of a complex variable when literal is selected as the type of initial value of a variable
Open the XML Data Wizard as described in Initializing a Variable. The following dialog displays:
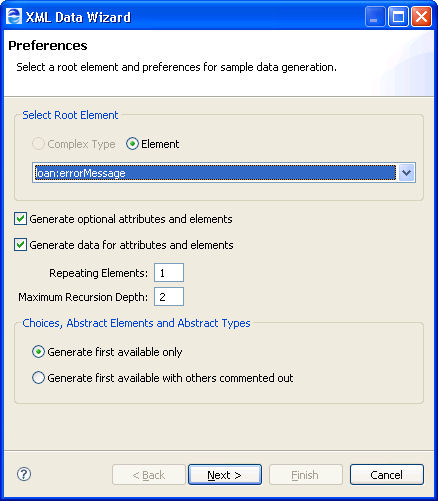
Make selections on the Preferences page as follows:
Selection | Description |
|---|
Select Root Element |
Complex Type or Element | Complex type or element is pre-selected based on the variable selected. You can select any matching type or element from the picklist. |
Generate optional attributes and elements | If the schema definition includes optional attributes (that is, use="optional"), and elements (that is, minOccurs="0"), you can include them in the data file, if desired. If you do not include them, you can experience a selection failure fault when you run the process, depending on the query used in selecting elements. |
Generate data for attributes and elements | Select this to generate appropriate values for elements and attributes. In some cases, such as derived simple types with regular expression patterns, the values are not schema valid. In most cases, the values provide a reasonable starting point for you to edit as necessary. If the element or attribute contains a fixed or default value it is automatically used. If a referenced type contains an enumerated restriction then the first value is selected from this restriction. Deselect this to generate empty elements and attributes. Generating elements without data does not produce a schema-valid sample. For variable initialization and copy operations, you can add your own values in the Literal Contents edit box after generating the data. For Interfaces and Process Variables sample data, you can open the generated XML file and edit it. |
Repeating Elements | For variables with repeating elements, such as a purchase order with multiple items, you can specify how many items to generate for that element. The default is one. |
Maximum Recursion Depth | Sets the recursion depth for a schema type that is recursive. The default depth is two, and the data generated is similar to the following: <foo>
<child />
<foo>
<child />
<foo/>
</foo>
</foo> |
Choices, Abstract Elements and Abstract Types |
Generate first available only | A Schema type can contain a choice construct that specifies that only one of the available choices can appear in the resulting document. The first available element is the first child element. A Schema element can contain one or more abstract elements. These elements cannot be created directly since they are abstract. Instead, the first available element is selected from its substitution group. The first available element is the first one encountered within any imported schemas. |
Generate first available with others commented out | Select this to generate all available elements, with all but the first generated within <!-- ---> tags. |
Example One: Repeating Elements
Given the following schema definitions for element=ns:items:
<xs:element name="items" type="imp:ItemsType" />
<xs:complexType name="ItemsType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element ref="imp:product" maxOccurs="unbounded" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:element name="product" type="imp:ProductType" />
<xs:complexType name="ProductType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="number" type="xs:integer" />
<xs:element name="name" type="xs:string" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
The following literal contents (or sample data file) is generated when Repeating Elements is set to three:
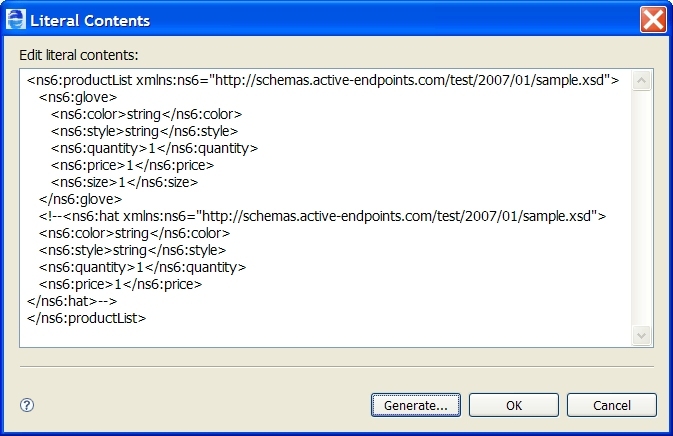
Example Two: Generate first available with others commented out
Given the following schema definitions for element=ns6:productList:
<xs:element name="productList">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element ref="tns:product"
maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="product" type="tns:ProductType"
abstract="true"/>
<xs:element name="hat" substitutionGroup="tns:product"
type="tns:ProductType"/>
<xs:element name="glove" substitutionGroup="tns:product"
type="tns:SubProductType"/>
<xs:complexType name="ProductType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="color" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="style" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="price" type="xs:decimal"/>
<xs:element name="quantity" type="xs:positiveInteger"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="SubProductType">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="tns:ProductType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="size" type="xs:int" />
</xs:sequence>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
The following literal contents (or sample data file) is generated :