DTM Processing
When you run a session, the DTM process reads source data and passes it to the transformations for processing. To help understand DTM processing, consider the following DTM process actions:
- •Reading source data. The DTM reads the sources in a mapping at different times depending on how you configure the sources, transformations, and targets in the mapping.
- •Blocking data. The DTM sometimes blocks the flow of data at a transformation in the mapping while it processes a row of data from a different source.
- •Block processing. The DTM reads and processes a block of rows at a time.
Reading Source Data
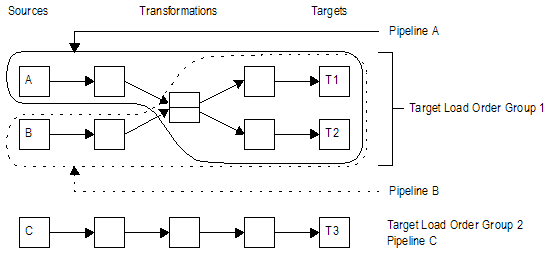
Mappings contain one or more target load order groups. A target load order group is the collection of source qualifiers, transformations, and targets linked together in a mapping. Each target load order group contains one or more source pipelines. A source pipeline consists of a source qualifier and all of the transformations and target instances that receive data from that source qualifier.
By default, the DTM reads sources in a target load order group concurrently, and it processes target load order groups sequentially. You can configure the order that the DTM processes target load order groups.
The following figure shows a mapping that contains two target load order groups and three source pipelines:
In the mapping, the DTM processes the target load order groups sequentially. It first processes Target Load Order Group 1 by reading Source A and Source B at the same time. When it finishes processing Target Load Order Group 1, the DTM begins to process Target Load Order Group 2 by reading Source C.
Blocking Data
You can include multiple input group transformations in a mapping. The DTM passes data to the input groups concurrently. However, sometimes the transformation logic of a multiple input group transformation requires that the DTM block data on one input group while it waits for a row from a different input group.
Blocking is the suspension of the data flow into an input group of a multiple input group transformation. When the DTM blocks data, it reads data from the source connected to the input group until it fills the reader and transformation buffers. After the DTM fills the buffers, it does not read more source rows until the transformation logic allows the DTM to stop blocking the source. When the DTM stops blocking a source, it processes the data in the buffers and continues to read from the source.
The DTM blocks data at one input group when it needs a specific row from a different input group to perform the transformation logic. After the DTM reads and processes the row it needs, it stops blocking the source.
Block Processing
The DTM reads and processes a block of rows at a time. The number of rows in the block depend on the row size and the DTM buffer size. In the following circumstances, the DTM processes one row in a block:
- •Log row errors. When you log row errors, the DTM processes one row in a block.
- •Connect CURRVAL. When you connect the CURRVAL port in a Sequence Generator transformation, the session processes one row in a block. For optimal performance, connect only the NEXTVAL port in mappings.
- •Configure array-based mode for Custom transformation procedure. When you configure the data access mode for a Custom transformation procedure to be row-based, the DTM processes one row in a block. By default, the data access mode is array-based, and the DTM processes multiple rows in a block.