Exception Management Workspaces
The Analyst tool uses workspaces to organize the different types of data operations that you can perform.
The Analyst tool lists the tasks that you own in the My Tasks view of the Start workspace. When you open the task, the Analyst tool displays the task records in the Exceptions workspace.
Start Workspace
The Start workspace displays the tasks that own and any task that you administer. Use the Start workspace options to open tasks, to perform actions on tasks, and to review the task metadata.
The user role that you use to log in to the Analyst tool determines the tasks that you can view in the Start workspace. Select the My Tasks view to display the tasks that you own. Select the Task Administration view to display any task that you administer. You can administer tasks if the workflow that creates the tasks identifies you as a business administrator.
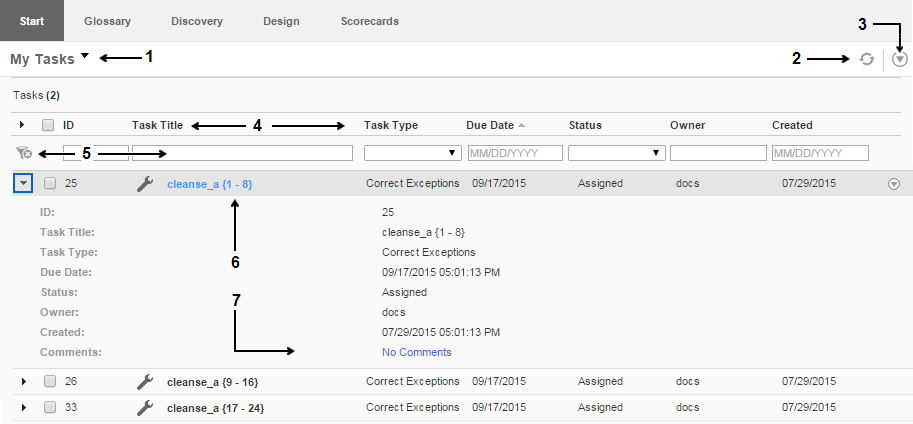
The following image shows a list of tasks in the My Tasks view:
The My Tasks view includes the following options:
- 1. My Tasks and Task Administration options. Toggle the workspace view between the tasks that you own and any task that you administer. You can open a task from the My Tasks view and from the Task Administration view.
- 2. Refresh. Refresh the workspace data.
- 3. Actions menu. Open a list of actions that you can perform on the tasks that you select.
- 4. Column headings. List the names of the columns that describe the task instances.
- 5. Filter. Use the values that you enter to filter the list of records.
- 6. Task name. Show the name of the task. To open a task, select the task name.
- 7. Comments. Open an editor that you can use to enter a comment or to read a comment about the task.
Start Workspace Column Headings
The Start workspace displays the tasks in a table. Each task is a row in the table. The table columns contain metadata about the tasks.
Use the following columns to review the metadata for the tasks that you own or administer:
- ID
- The unique identifier for the task instance. The identifier includes a value that identifies the Human task that generated the task instance.
- Task Title
- The name of the task. The task name identifies the step in the Human task that the generated the task data.
- The Task Title column includes a filter field that you can use to filter the list of task names. You can include wildcard characters with the filter string that you enter.
- If you add a wildcard character to a filter string, the Analyst tool returns the tasks that include the filter string in any position in the task name.
- Task Type
- The type of data operation that you can perform on the task data.
- The task can be one of the following types:
- - Correct exceptions. Examine and fix errors in the records.
- - Correct duplicates. Examine a cluster of duplicate records and create a preferred record from the values in the records.
- - Review exceptions. Review the work of another user in a task that corrects exceptions.
- - Review duplicates. Review the work of another user in a task that creates a preferred record from a cluster of records.
Note: The task types might include Voting tasks. Business Glossary users work on Voting tasks. Voting tasks are not a part of the exception management process.
- Due Date
- The deadline for the task. The Human task defines the due date for a correct exceptions task and a correct duplicates task. The Analyst tool calculates the due date for a correct exceptions task and a correct duplicates task.
- Status
- The status of the task
- The task can have one of the following statuses:
- - Created. The task has no owner.
- - Assigned. The task has an owner.
- Owner
- The name of the current task owner.
- Created
- The date on which the workflow created the task.
Exceptions Workspace
The Exceptions workspace is a temporary workspace that appears when you view or open a task. The Exceptions workspace contains a Data Editing tab and a Data Audit tab.
The Data Editing tab displays the task data and the options that you can use to update the records or clusters in the task. The tab also displays the metadata columns that the Analyst tool uses to track the updates that you and other users make to each record or cluster.
The Data Audit tab displays an audit trail of the changes that you and other users made to the task data. You can view the fields that users changed, the identity of the user who changed each record, and the date of the change.
When you finish work on a task, you can close the Exceptions workspace.