Connect Objects
The context of an object is critical information that you need to know. Axon derives the context of an object from the other objects it is connected to in different facets.
You can associate an object from one facet to another facet. The Impact tab of an object shows the connection of the object across many other facets. If you have edit permissions, you can connect the objects from the Impact tab.
If an object is part of a segment, the related objects must also belong to the same segment. You cannot connect or link objects of one segment with the objects of another segment. You can create cross-facet relationships within the same segment.
You can create unidirectional, bidirectional, and inferred connections between facets. Unidirectional connections start from one facet to another and not the other way around. Bidirectional connections start from either of the facets. Inferred connections link one facet to another through other facets.
To view a visual representation of connections between the facets that you can create from the Impact tab, refer to https://network.informatica.com/docs/DOC-18595
From the Impact tab of an object, you can perform the following tasks:
- •View and edit a connection.
- •Create a connection.
- •Search and add a connection.
View and Edit Modes
If you view an object in the View mode, you can see the facets to which the object is connected. If you view the same object in the Edit mode, you can see additional facets to which you can connect the object. For example, if you open a Data Set object, you can see the Policy facet in the View mode and the Policy, Client, and Legal Entity facets in the Edit mode.
The connections to objects in the facets are unidirectional. For example, you can edit the Impact tab of a Process object to connect the object to the System object. If you look at the connected System object, you can view the relationship, but cannot edit the relationship.
Create Connections
Users with the appropriate edit permissions can add or manage connections. Create a connection in the Edit mode. Use the + icon to add a connection, and the - icon to delete a connection. When you create a connection, the fields that appear depend on the facet type.
The following fields might appear when you create a connection:
Field | Type | Description |
|---|
Relationship Type | Required | The type of relationship between the object and facet. You can configure the list of the relationship types. |
Object | Required | The name of the object that you want to connect the active object to. |
Ref. | Optional | The reference number of the object that the object connects to. After you select an object, Axon automatically populates the reference number and ensures that the correct object is selected. |
Owner | Optional | The owner of the object that the object connects to. After you select an object, Axon automatically populates the owner. |
Description | Optional | Description of the relationships between the objects. |
Search and Add Connections
You can provide search criteria to find and add objects. To search and add objects, click the Search and Add button next to the Grid Settings. To find the objects that you want to add, select the Axon Status value or perform a keyword search.
After the search results appear, you can perform the following tasks:
- •Add each object one by one.
- •Remove a collection of object connections.
- •Add all the objects that belong to a hierarchy together based on the relationship type.
- •Add the additional or missing objects if all the hierarchical objects are added.
Unison Search Exceptions
When you run a Unison search, Axon searches for objects and their linked objects in all the available facets. However, there are some exceptions in Unison search for Process, Project, and Policy objects if they are directly connected to data sets and attributes.
You can create the following inferred connections:
- •Process to System and System to Data Set
- •Process to System and System to Attribute
- •Process to Glossary and Glossary to Data Set
- •Process to Glossary and Glossary to Attribute
- •Project to System and System to Data Set
- •Project to System and System to Attribute
- •Project to Glossary and Glossary to Data Set
- •Project to Glossary and Glossary to Attribute
- •Policy to System and System to Data Set
- •Policy to System and System to Attribute
You can also create the following direct connections:
- •Process to Data Set
- •Process to Attribute
- •Project to Data Set
- •Project to Attribute
- •Policy to Data Set
- •Policy to Attribute
If a direct connection does not exist, Axon displays the linked objects in the usual way. If a direct connection exists between these objects, the Unison search results vary. If a direct connection exists between two objects and if you search one of these objects, Axon displays the related objects only if all the connection paths exist. For example, consider a data set that is directly connected to a project. If you search for the data set, Axon displays the linked project only if the project has the following connection paths to the data set:
- •Project to Data Set
- •Project to System and System to Data Set
- •Project to Glossary and Glossary to Data Set
Scenario 1: Search for a Data Set
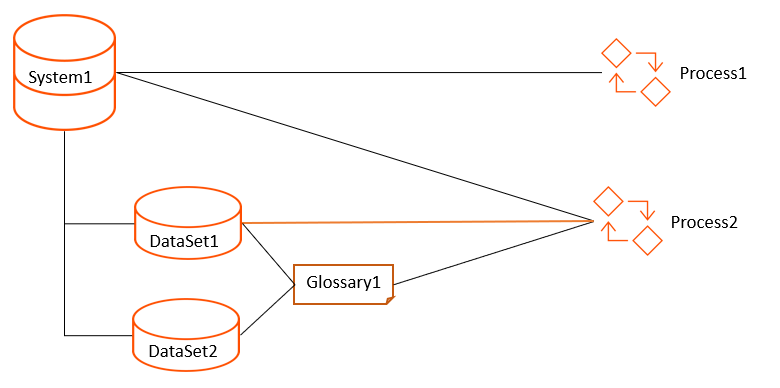
The following image shows that DataSet1 is directly connected to Process2:
When you search for DataSet1, Unison search returns Process1 and Process2. DataSet1 is directly connected to Process2, and the connections from System1 to Process2 and Glossary1 to Process2 are also present. DataSet1 is connected to Process1 through System1.
When you search for DataSet2, Unison search returns only Process1. DataSet2 is connected to Process1 through System1. Though DataSet2 is connected to Process2 via Glossary1 and System1, Process2 is directly connected to DataSet1. Because of this direct connection to another data set within the same system, the Process2 does not appear in the search results when you search for DataSet2.
Scenario 2: Search for an Attribute
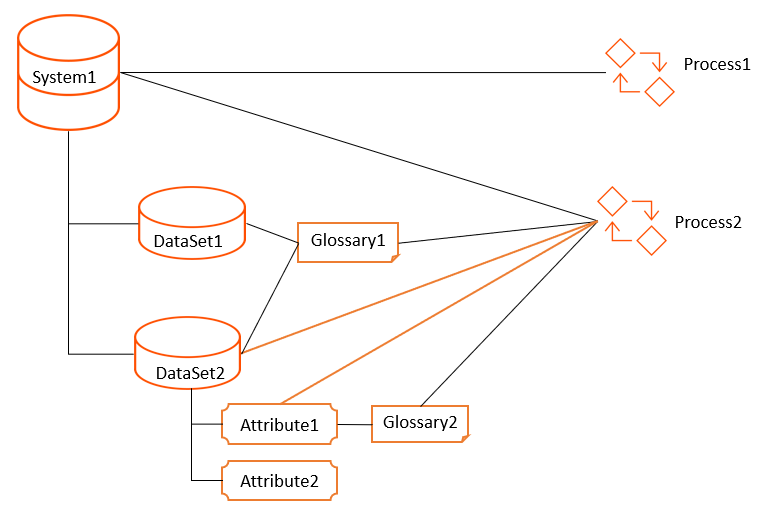
The following image shows that Attribute1 is directly connected to Process2:
When you search for Attribute1, Unison search returns Process1 and Process2. Attribute1 is directly connected to Process2, and the connections from System1 to Process2 and Glossary1 to Process2 are also present. Attribute1 is connected to Process1 through System1.
When you search for Attribute2, Unison search returns only Process1. Attribute2 is connected to Process1 through System1. Though Attribute2 is connected to Process2 via System1, Process2 is directly connected to Attribute2. Because of this direct connection to another attribute within the same system, the Process2 does not appear in the search results when you search for Attribute2.
Scenario 3: Search for a Process
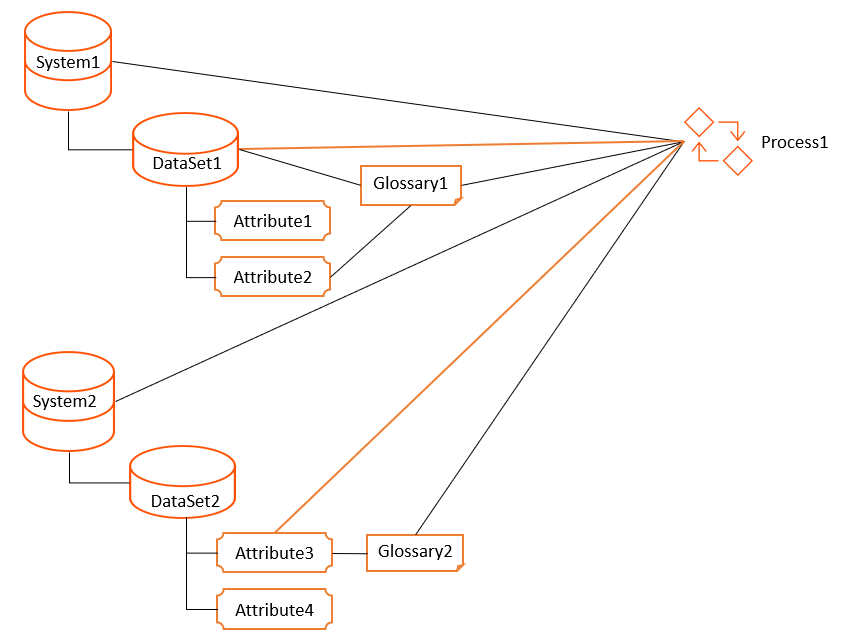
The following image shows that DataSet1 and Attribute3 are directly connected to Process1:
When you search for Process1, Unison search returns DataSet1, DataSet2, Attribute1, Attribute2, and Attribute3 based on the following logic:
- •The search results show DataSet1 because Process1 is directly connected to DataSet1, and the connections from System1 to DataSet1 and Glossary1 to DataSet1 are also present.
- •The search results show DataSet2 because Process1 is connected to DataSet2 via System2. The direct connection from Process1 to DataSet1 is not considered because DataSet1 belongs to another system.
- •The search results show Attribute1 because Process1 is connected to Attribute1 via System1.
- •The search results show Attribute2 because Process1 is connected to Attribute2 via Glossary1 and System1.
- •The search results show Attribute3 because Process1 is directly connected to Attribute3, and the connections from System2 to Attribute3 and Glossary2 to Attribute3 are also present.
- •The search results do not return Attribute 4. Though Process1 is connected to Attribute4 via System2, there is a direct connection from Process1 to another attribute within the same system.
The Unison search exception scenarios apply to Process, Project, and Policy objects.