Target
The target describes the Hive or HDFS target where you want to ingest the source tables from the relational database.
You specify different target properties depending on the scenario that you select in the specification definition. If you configure the specification to ingest data from a relational database to Hive, you configure a Hive connection and Hive table properties to define the target. If you configure the specification to ingest data from a relational database to HDFS, you configure an HDFS connection and an ingestion directory to define the target.
The mass ingestion solution ingests all data to the target. The mass ingestion solution does not provide the option to append data that has been recently updated. Each time that you run the mass ingestion specification, the existing data in the Hive or HDFS target is deleted and replaced with the data configured in the ingestion job.
Configuring a Hive Target
Configure a Hive target to ingest data to a Hive table. When you configure the mass ingestion specification to ingest data to a Hive target, you configure a Hive connection and Hive properties to define the target.
You can ingest data to an internal or external Hive table. Internal Hive tables are managed by Hive. External Hive tables are unmanaged tables. You can specify an external location for an external Hive table such as Amazon S3, Azure Blob, HDFS, WASB, or ADLS.
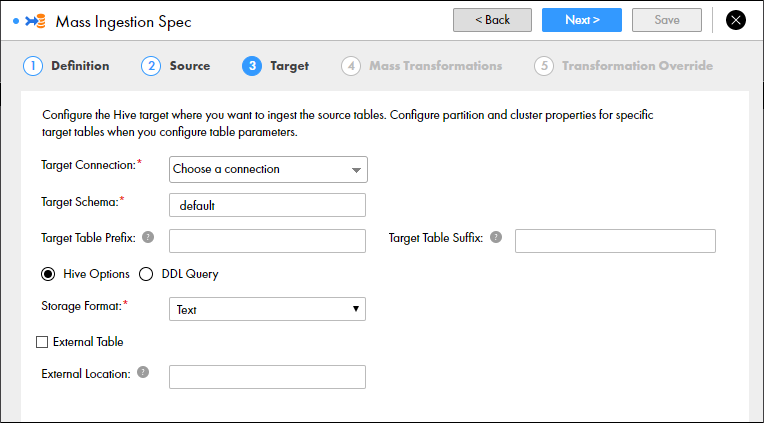
The following image shows the Target page for a Hive target:
The following table describes the properties that you can configure to define the Hive target:
Property | Description |
|---|
Target Connection | Required. The Hive connection used to find the Hive storage target. If changes are made to the available Hive connections, refresh the browser or log out and log back in to the Mass Ingestion tool. |
Target Schema | Required. The schema that defines the target tables. |
Target Table Prefix | The prefix added to the names of the target tables. Enter a string. You can enter alphanumeric and underscore characters. The prefix is not case sensitive. |
Target Table Suffix | The suffix added to the names of the target tables. Enter a string. You can enter alphanumeric and underscore characters. The prefix is not case sensitive. |
Hive Options | Select this option to configure the Hive target location. |
DDL Query | Select this option to configure a custom DDL query that defines how data from the source tables is loaded to the target tables. |
Storage Format | Required. The storage format of the target tables. You can select Text, Avro, Parquet, or ORC. Default is Text. |
External Table | Select this option if the table is external. |
External Location | The external location of the Hive target. By default, tables are written to the default Hive warehouse directory. A sub-directory is created under the specified external location for each source that is ingested. For example, you can enter /temp. A source table named PRODUCT is ingested to the external location /temp/PRODUCT/ |
Configure partition and cluster properties for specific target Hive tables when you configure the transformation override.
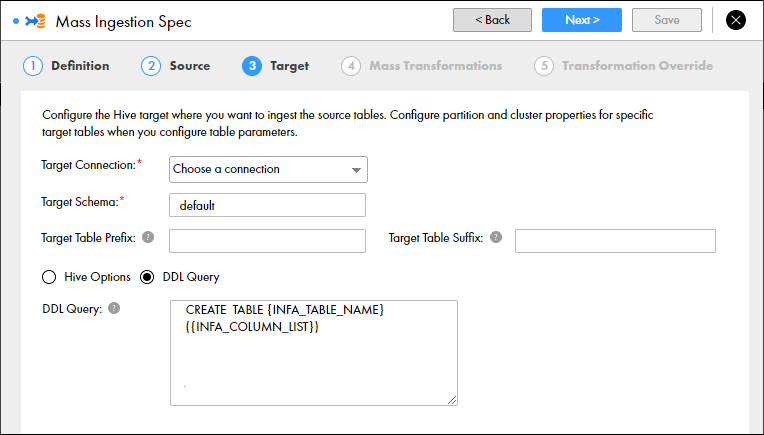
DDL Query
When you configure a mass ingestion specification to ingest data to a Hive target, you can configure a custom DDL query to define how data from the source tables is loaded to the target tables.
You can define the DDL query to customize the target table or specify additional parameters. The target table contains the columns that you define in the DDL query.
To define a DDL query, use SQL statements and placeholders. Use the placeholders to fetch the table name, column list, and column names. The Data Integration Service substitutes the placeholders with actual values at run time according to the tables that you ingest. You must enclose the placeholders within curly brackets. For example, {INFA_TABLE_NAME}.
You can use the following placeholders:
- INFA_TABLE_NAME
- Fetches the target table name at run time.
- INFA_COLUMN_LIST
- Fetches a list of columns in the target table at run time.
For example, you might ingest a table CUSTOMER. To define how you want to ingest the table in the target, you can enter the following DDL query:
CREATE TABLE {INFA_TABLE_NAME} ({INFA_COLUMN_LIST}) CLUSTERED BY (LAST_NAME) INTO 10 BUCKETS STORED AS TEXT
At run time, the Data Integration Service substitutes {INFA_TABLE_NAME} with CUSTOMER, and it substitutes {INFA_COLUMN_LIST} with the list of columns that appear in the table CUSTOMER. The Data Integration Service might expand the DDL query to the following query:
CREATE TABLE CUSTOMER (FIRST_NAME STRING, LAST_NAME STRING, EMAIL STRING, GENDER STRING, CREDIT_CARD DECIMAL (38,0), CREDIT_CARD_TYPE STRING, STATE, STRING, USSTATE STRING, CITY STRING) CLUSTERED BY (LAST_NAME) INTO 10 BUCKETS STORED AS TEXT
Note: You cannot use a placeholder to specify the partition columns and clustered by columns. When you specify the partition columns and clustered by columns, enter the column name in the DDL query.
The following image shows the option to configure a DDL query for a Hive target:
Configuring an HDFS Target
Configure an HDFS target to ingest data to a flat file on HDFS. When you configure the mass ingestion specification to ingest data to an HDFS target, you configure an HDFS connection and an ingestion directory to define the target.
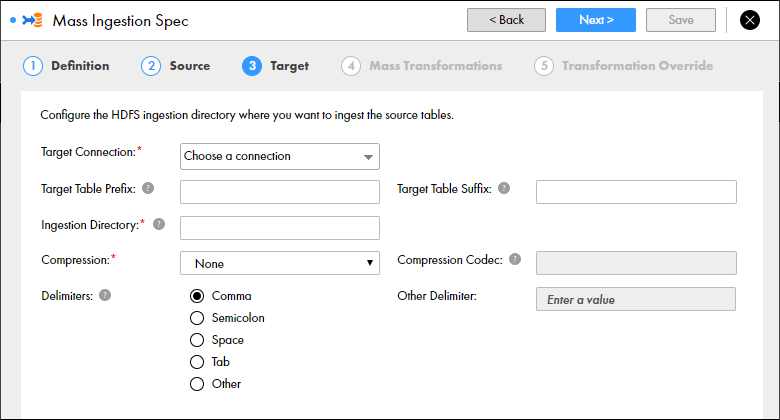
The following image shows the Target page for an HDFS target:
The following table describes the properties that you can configure to define the HDFS target:
Property | Description |
|---|
Target Connection | Required. The HDFS connection used to find the HDFS storage target. If changes are made to the available HDFS connections, refresh the browser or log out and log back in to the Mass Ingestion tool. |
Target Table Prefix | The prefix added to the names of the target files. Enter a string. You can enter alphanumeric and underscore characters. The prefix is not case sensitive. |
Target Table Suffix | The suffix added to the names of the target files. Enter a string. You can enter alphanumeric and underscore characters. The prefix is not case sensitive. |
Ingestion Directory | Required. The target directory on HDFS. A sub-directory is created under the ingestion directory for each source that is ingested. If the specified directory already exists, the directory is replaced. For example, you can enter /temp. A source table named PRODUCT is ingested to the directory /temp/PRODUCT/ |
Compression | Required. The compressed file format that stores the target files. You can select None, Gzip, Bzip2, LZO, Snappy, or Custom. If you select Custom, enter the compression codec. Default is None. |
Compression Codec | If you select custom compression, enter the fully qualified class name implementing the Hadoop CompressionCodec interface. |
Delimiters | The delimiters used to separate data in the target files. You can select comma, semicolon, space, tab, or other. If you select Other, you can define a custom delimiter. |
Other Delimiter | Required if you choose Other Delimiter. Enter a custom delimiter. |
Compression Codec
When you configure a mass ingestion specification to ingest data to an HDFS target directory, you can configure a compression codec to write the ingested data to a compressed file.
You can select one of the following compression options:
- •Gzip
- •Bzip2
- •LZO
- •Snappy
- •Custom
If you specify a custom compression codec, you must specify the fully qualified class name implementing the Hadoop CompressionCodec interface.