Stateful Computing
Stateful computing involves storing and retrieving state while evaluating expressions in an Expression transformation.
You can use variable port definitions in Expression transformations to perform stateful computing in a streaming mapping.
Use variable port definitions to perform the following tasks:
- •Calculate and store the state in stateful variables when an event arrives.
- •Use the stored state and input to compute the output.
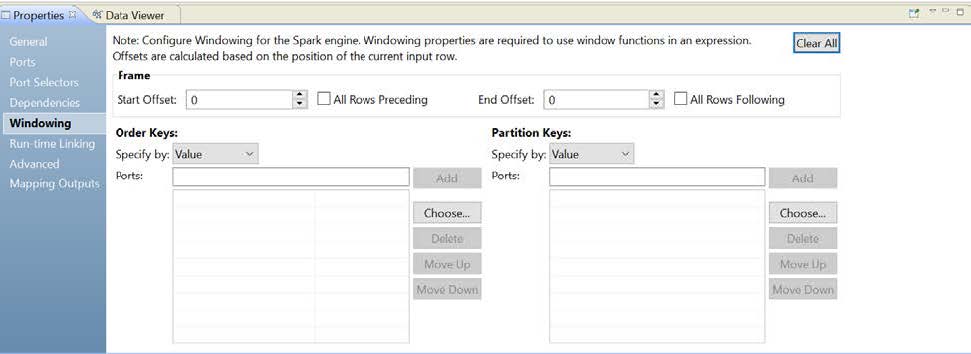
When you configure the Expression transformation, configure the partition keys on the Windowing tab. When you define variable ports in an Expression transformation, you can optionally specify a partition key that uses one or more input ports. The partition keys determine which columns to group the data by while performing stateful computing. The stored state will have one value for every stateful variable for each value of the partition key.
The evaluation of the ports is ordered. The output ports are computed after the variable ports are computed and contain updated values of variables.
When you configure windowing properties, you define a stateful expression in the Expression transformation. Streaming mappings support all the expression transform function except Window functions and aggregate functions.
For more information about guidelines for configuring variable ports, see the Informatica Developer Transformation Guide.
Partitioning Configuration
Configure partitioning by specifying one or more columns under partition keys on the Windowing tab.
The following image shows the Windowing tab:
Optionally, configure the partition keys to separate the input rows into different partitions. Configure the partition keys to define partition boundaries, rather than performing the calculation across all inputs. If you do not define partition keys, all the data is included in the same partition. The variable values stored will be global and every row can read and update the same set of variables.
You can specify the partition keys by value or parameter. Select Value to use port names.
The following table lists the data type support for variable ports:
Data Type | Initial State Value |
|---|
String | EMPTY_STRING |
Integer | 0 |
Double | 0.0 |
Long | 0 |
Text | EMPTY_STRING |
Decimal | 0.0 |
Example
You want to compute average temperature of cities in a region. Add an Expression transformation to your streaming mapping.
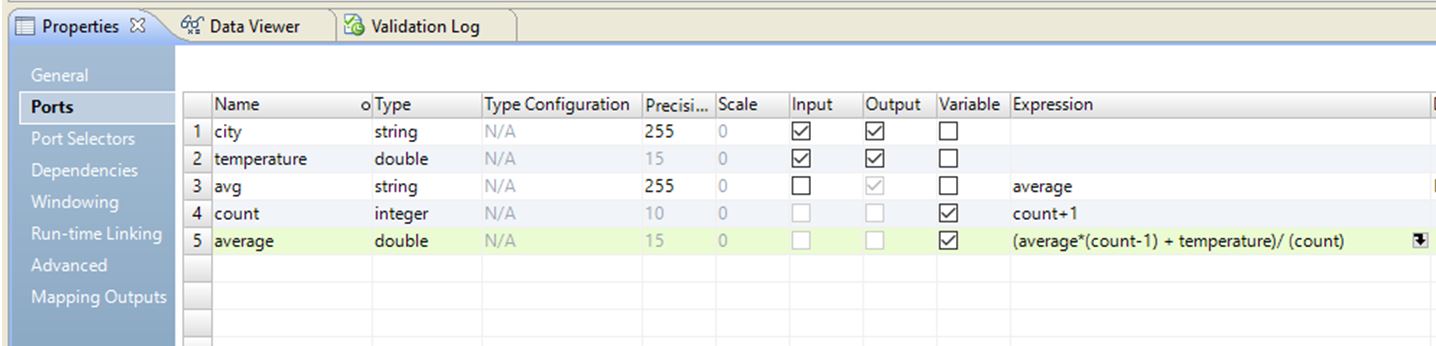
Configure the following ports in the transformation:
- •city. Input port of string data type.
- •temperature. Input port of double data type.
- •avg. Output port that displays the average temperature.
- •count. Variable port of integer data type with expression ‘count+1’.
- •average. Variable port of double data type with expression (average * (count-1) + temperature/(count)
You partition the data by "city". The "average" corresponds to previously stored value for the "average" and is computed with each update in the value of "count". Since "count" is already incremented when "average" is evaluated, specify "count-1" in the expression to get the new average.
The following image shows an Expression transformation: