Partitioned Flat File Targets
When a mapping that is enabled for partitioning writes to a flat file target, the Data Integration Service can use multiple threads to write to the file target.
The Data Integration Service can create partitions for a flat file or a file in Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS).
You can configure a flat file data object to have either a file or command output type. When a flat file data object has the file output type, the Data Integration Service writes the target data to a flat file. If multiple threads write to the flat file target, each thread writes the target output to a separate file. Each thread uses the following format to name the file:
<output_file_name><partition_number>.out
For example, three threads might write to files named MyOutput1.out, MyOutput2.out, and MyOutput3.out.
You can configure multiple output file directories to optimize performance, or you can configure the flat file data object to write to a single merge file.
When a flat file data object has the command output type, the Data Integration Services outputs the target data to a command or to a merge command instead of a flat file or a merge file. If multiple partitions write to the flat file target, you can configure a command to process target data for a single partition or to process merge data for all target partitions.
Optimize Output File Directories for Partitioned File Targets
By default when a flat file data object has a file output type, each thread writes the target output to a separate file. For optimal performance when multiple threads write to a file target, configure multiple output file directories.
When multiple threads write to a single directory, the mapping might encounter a bottleneck due to input/output (I/O) contention. An I/O contention can occur when threads write data to the file system at the same time.
When you configure multiple directories, the Data Integration Service determines the output directory for each thread in a round-robin fashion. For example, you configure a flat file data object to use directoryA and directoryB as target directories. If the Data Integration Service uses four threads to write to the file target, the first and third writer threads write target files to directoryA. The second and fourth writer threads write target files to directoryB.
If the Data Integration Service does not use multiple threads to write to the target, the service writes the output file to the first listed directory.
Configure the output file directories in the Advanced properties for the flat file data object. Find the Output File Directory property in the Runtime: Write section. By default, the property is configured to use the system parameter value defined for the Data Integration Service. Use the default TargetDir system parameter value if an administrator entered multiple directories separated by semicolons for the Target Directory property for the Data Integration Service.
You can enter a different value to configure multiple output file directories specific to the flat file data object. Enter multiple directories separated by semicolons for the property or for the user-defined parameter assigned to the property.
Merge Options for Partitioned File Targets
By default when a flat file data object has a file output type, each thread writes the target output to a separate file. You can merge target data for the partitions. When you merge target data, the Data Integration Service creates a single merge file for all target partitions.
Configure the merge options in the Advanced properties for the flat file data object. Find the merge properties in the Runtime: Write section.
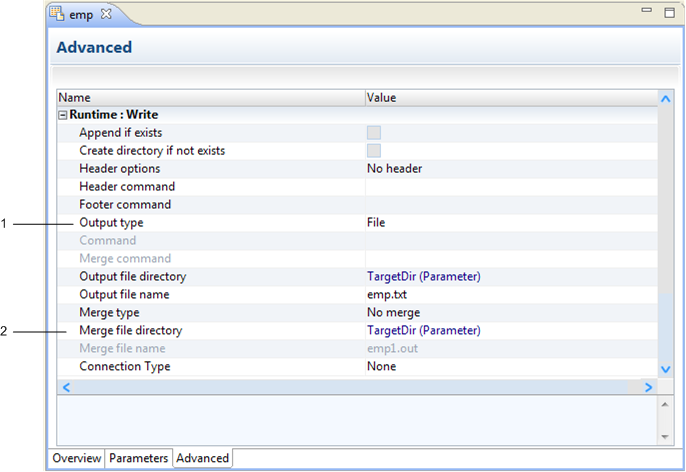
The following image shows the merge options in the advanced properties for a flat file data object:
- 1. File output type
- 2. Merge options
Select one of the following options for the Merge Type property:
- No merge
The Data Integration Service concurrently writes the target output to a separate file for each partition.
Default option.
- Sequential
- The Data Integration Service creates an output file for each partition and then merges them into a single merge file. The Data Integration Service creates the individual target files using the output file name and output file directory values. The Data Integration Service sequentially adds the output data for each partition to the merge file, in the order that each writer thread completes. For example, if the writer thread for Partition2 finishes before the thread for Partition1, the Data Integration Service adds the data to the merge file in the following order: Partition2, Partition1.
- File list
- The Data Integration Service creates a target file for each partition and creates a file list that contains the paths of the individual files. The Data Integration Service creates the individual target files using the output file name and output file directory values. If you write the target files to the merge directory or a directory under the merge directory, the file list contains relative paths. Otherwise, the file list contains absolute paths. Use this file as a source file if you use the target files as source files in another mapping.
- Concurrent
- The Data Integration Service concurrently writes the data for all target partitions to the merge file. It does not create intermediate files for each partition. Because the Data Integration Service writes to the merge file concurrently for all partitions, the order of the data in the merge file might not be sequential.
If you configure the flat file data object to merge target data, you can optionally edit the default values for the Merge File Directory and Merge File Name properties.
If you configure the flat file data object to merge target data and the Data Integration Service does not create partitions for the target, the Data Integration Service ignores the merge options. The service writes to the file defined in the Output File Name and Output File Directory properties.
Commands for Partitioned File Targets
When a flat file data object has a command output type, you can use a command to process target data for a single partition or to process merge data for all target partitions in a mapping. The Data Integration Service sends the data to a command or to a merge command instead of a flat file or a merge file.
Configure the command that processes data for partitions in the Advanced properties for the flat file data object. Find the command properties in the Runtime: Write section.
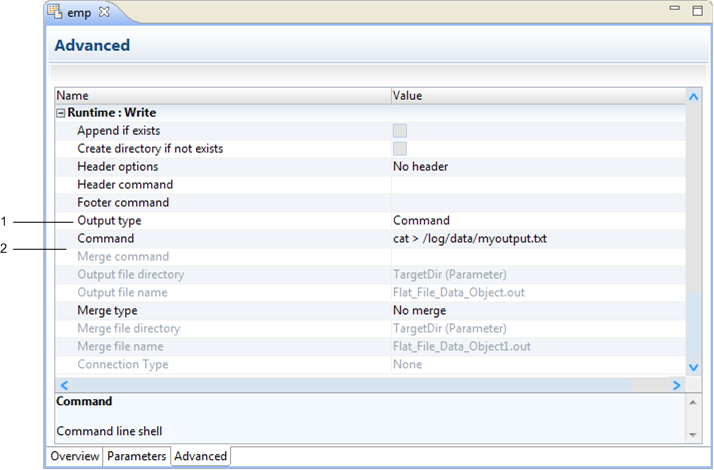
The following image shows a flat file data object configured to use a command to process target data for a single partition:
- 1. Command output type
- 2. Command options
On UNIX, use any valid UNIX command or shell script. On Windows, use any valid DOS or batch file.
You can use a command to process the following types of target data:
- Data for a single partition
Enter a command that each writer thread runs separately. Each thread sends the target data to the command when the mapping runs. Each thread runs the same command with a different set of data.
When you enter the command, you must consider the operating system on which the mapping runs. For example, if you enter the command cat > /log/data/myoutput.txt, multiple threads write to the same file which could cause an operating system error. If you enter the command cat >> /log/data/myoutput.txt, multiple threads append data to the same file which is less likely to cause an operating system error.
To send the target data for a single partition to a command, select command for the Output Type property, and select no merge for the Merge Type property. Enter a command for the Command property.
- Merge data for all partitions
Enter a merge command that processes the merge data for all writer threads. The Data Integration Service must use a concurrent merge type for a command to process merge data. Each thread concurrently sends target data to the merge command when the mapping runs. The merge command runs once with all of the data. The command might not maintain the order of the target data.
To send merge data for all partitions to a merge command, select command for the Output Type property, and select concurrent for the Merge Type property. Enter a command for the Merge Command property.