Selection Rules and Port Selectors
When a transformation has generated ports, you need to configure the transformation to run successfully when the generated ports change. You can use a port selector to determine which ports to use in a dynamic expression, a lookup condition, or a joiner condition.
A port selector is a set of selection rules that determine ports. You reference a port selector in an expression. When the generated ports change in a dynamic mapping, the port selector can contain different ports in it. You can create a port selector in an Expression transformation, a Lookup transformation, or a Joiner transformation. These transformations contain expressions that can reference all the ports in the port selector.
You can configure a port selector in the following mapping objects:
- Expression transformation
- You can reference a port selector in a dynamic expression. When you reference a port selector in the expression, the expression runs against each port in the port selector. The dynamic expression returns a result to a separate output port for each port in the port selector. If the transformation has multiple expressions that reference port selectors, the transformation returns additional output ports for each expression.
- Joiner transformation
- You can reference two port selectors in a join condition. Define a port selector for the master group and a port selector for the detail group. The Data Integration Service compares each port in the master group to the port in the detail group based on the order of the ports in the port selector. You can choose one type of operator to compare each pair of ports. Each port selector must have the same number of ports.
For example, you configure a port selector called Master-SelectorX that contains the ports A, B, and C. You configure Detail-SelectorY that contains the ports D, E, F. If the join condition is Master-SelectorX = Detail-SelectorY, then the Developer tool creates the following join condition: A = D AND B = E AND C = F.
- Lookup transformation
- You can configure a port selector for the ports in a lookup condition. The Data Integration Service compares each port in the input port selector to a port in the lookup port selector based on the order of the ports in each port selector. Each port selector must have the same number of ports.
- Write transformation
You can configure a port selector for the ports in the Write transformation.
When you write data to a relational or Hive target, you can choose to create or replace the target table at run time. You can define a DDL query based on which the Data Integration Service must create or replace the target table at run time. You can also configure a port selector in the DDL query.
Port Selector Configuration
When you configure a port selector, you define selection rules to determine which generated ports to include. The selection rules are similar to the input rules that you can configure for dynamic ports.
A port selector can include static or generated ports. Configure a port selector on the Port Selector tab.
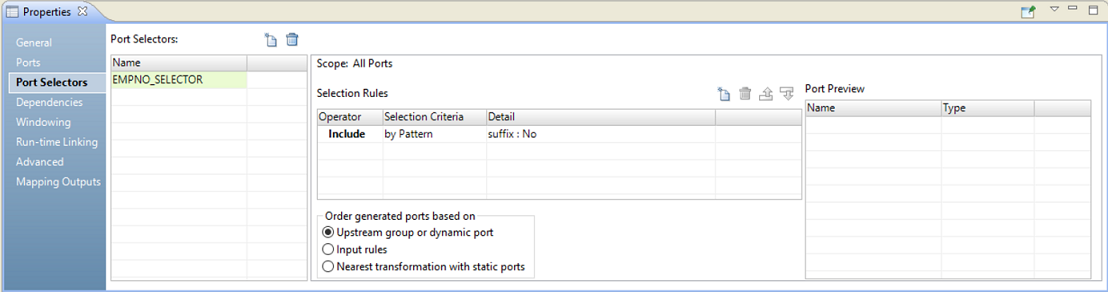
The following image shows the Port Selector tab:
Configure the following properties for a port selector:
- Name
- Identifies the port selector. You can create multiple port selectors in a transformation and reference them in expressions.
- Scope
- Identifies a group of ports that the port selector applies to. You must choose the scope when you create a port selector for a Joiner or a Lookup transformation. These transformations have multiple input groups. The Joiner transformation has a Master or a Detail scope. The Lookup transformation has an Import or a Lookup scope. The Expression transformation has one input group. The scope is always All Ports.
- Selection Rules
- Determines the ports to include in the port selector. When you create the selection rules, the Port Preview panel shows the ports that qualify from the current input ports. These ports might change. Configure the selection rules to accommodate ports from different sources.
Selection Rules
The selection rules associated with a port selector determine the ports to include in the port selector.
When you create the selection rules, the Port Preview panel shows the ports that qualify from the current input ports. These ports might change. Configure the selection rules to accommodate ports from different sources.
Create selection rules based on the following criteria:
- Operator
- Includes or excludes the ports that selection rules return. Default is include. You must include ports before you can exclude ports.
- Selection Criteria
- The type of selection rule you want to create. You can create a rule based on the column name, port type, pattern, or complex data type definition. To include ports based on the column name, search for specific names or search for a pattern of characters in the name.
- Detail
- The values to apply to the selection criteria. If the selection criteria is by column name, configure the string or name to search for. If the selection criteria is by port type, select the port types to include.
The following table describes the selection criteria and how to specify the details for the criteria:
Selection Criteria | Description | Detail |
|---|
All | Includes all ports. | No details required. |
Name | Filters ports based on the port name. | Select the port names from a list of values or use a parameter of type Port or Port List. |
Type | Filters ports based on the data type of each port. | Select data types from a list. |
Pattern | Filters ports by a string of characters in the name or by a regular expression. | Choose prefix, suffix, or regular expression as the pattern type for the port name. Then, enter a value for the pattern or use a parameter of type String. |
Complex Data Type Definition | Filters ports by a complex data type definition. | Choose prefix, suffix, or regular expression as the pattern type for the complex data type definition. Then, enter a value for the pattern or use a parameter of type String. |
Example - Selection Rules and Port Selectors
You configure the mapping to use dynamic sources, but the column that contains salary information in each source file has a different name. The column names for the different sources are Salary, Monthly_Salary, or Base_Salary.
You perform the following tasks to run the expression with any of the salary port names:
- 1. You create a port selector named "Salary_PortSelector."
- 2. You create a selection rule to accept any port name with the suffix of "Salary."
- 3. Configure the expression to include the port selector name instead of a specific column name. The expression has the following syntax:
Salary_PortSelector * 12