
Property | Description |
|---|---|
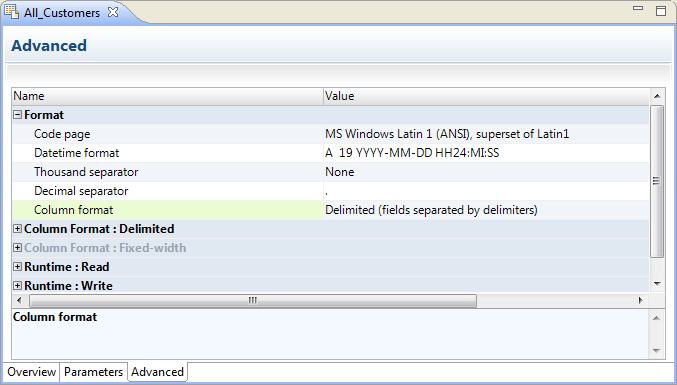
Code page | Code page of the flat file data object. For source files, use a source code page that is a subset of the target code page. For lookup files, use a code page that is a superset of the source code page and a subset of the target code page. For target files, use a code page that is a superset of the source code page Default is "MS Windows Latin 1 (ANSI), superset of Latin 1." |
Datetime format | Defines the display format and the field width for datetime values. Default is "A 19 YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS." |
Thousand separator | Thousand separator for numeric values. Default is None. |
Decimal separator | Decimal separator for numeric values. Default is a period (.). |
Column Format | Format for the flat file, either delimited or fixed-width. |
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Delimiters | Character used to separate columns of data. Click the Delimiters field to select a character or to assign a parameter to the property. Delimiters must be printable characters and must be different from the text qualifier and the escape character if selected. Default is Comma. |
Text qualifier | Quote character that defines the boundaries of text strings. If you select a quote character, the Developer tool ignores delimiters within a pair of quotes. Default is No Quotes. |
Start import at line | Row at which the Data Integration Service starts importing data. Use this option to skip header rows. Default is 1. |
Row delimiter | Octal code for the character that separates rows of data. Default is line feed, \012 LF (\n). Note: The row delimiter applies to reading source data. When the Data Integration Service writes to a target file, it always uses the default delimiter, \n. |
Escape character | Character used to escape a delimiter character in an unquoted string if the delimiter is the next character after the escape character. If you specify an escape character, the Data Integration Service reads the delimiter character as a regular character embedded in the string. Note: You can improve mapping performance slightly if the source file does not contain quotes or escape characters. |
Retain escape character in data | Includes the escape character in the output string. Default is disabled. |
Treat consecutive delimiters as one | Causes the Data Integration Service to treat one or more consecutive column delimiters as one. Otherwise, the Data Integration Service reads two consecutive delimiters as a null value. Default is disabled. |
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Null character type | Null character type, either text or binary. |
Null character value | Character used to represent a null value. The null character can be any valid character in the file code page or any binary value from 0 to 255. |
Repeat null character | For source files, causes the Data Integration Service to read repeat null characters in a single field as one null value. For target files, causes the Data Integration Service to write as many null characters as possible into the target field. If you do not enable this option, the Data Integration Service enters one null character at the beginning of the field to represent a null value. Default is disabled. |
Start import at line | Row at which the Data Integration Service starts importing data. Use this option to skip header rows. Default is 1. |
Number of bytes to skip between records | Number of bytes between the last column of one row and the first column of the next. The Data Integration Service skips the entered number of bytes at the end of each row to avoid reading carriage return characters or line feed characters. Enter 1 for UNIX files and 2 for DOS files. Default is 2. |
Line sequential | Causes the Data Integration Service to read a line feed character or carriage return character in the last column as the end of the column. Select this option if the file uses line feeds or carriage returns to shorten the last column of each row. Default is disabled. |
Strip trailing blanks | Strips trailing blanks from string values. Default is disabled. |
User defined shift state | Allows you to select the shift state for source columns in the Columns properties. Select this option when the source file contains both multibyte and single-byte data, but does not contain shift-in and shift-out keys. If a multibyte file source does not contain shift keys, you must select a shift key for each column in the flat file data object. Select the shift key for each column to enable the Data Integration Service to read each character correctly. Default is disabled. |
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Input type | Type of source input. You can choose the following types of source input:
|
Source type | Indicates source type of files with the same file properties. You can choose one of the following source types:
|
Source file name | File name of the flat file source. |
Source file directory | Directory where the flat file sources exist. The machine that hosts Informatica services must be able to access this directory. Default is the SourceDir system parameter. |
Concurrent Read Partitioning | Order in which multiple partitions read input rows from a source file. If the Data Integration Service does not create partitions for the mapping, it ignores this value. Select one of the following options:
|
Connection Type | The type of connection. Select from the following options:
Default is None. |
Command | Command used to generate the source file data. Use a command to generate or transform flat file data and send the standard output of the command to the flat file reader when the mapping runs. The flat file reader reads the standard output as the flat file source data. Generating source data with a command eliminates the need to stage a flat file source. Use a command or script to send source data directly to the Data Integration Service instead of using a pre-mapping command to generate a flat file source. You can also use a command to generate a file list. For example, to use a directory listing as a file list, use the following command: cd MySourceFiles; ls sales-records-Sep-*-2005.dat |
Truncate string null | Strips the first null character and all characters after the first null character from string values. Enable this option for delimited flat files that contain null characters in strings. If you do not enable this option, the Data Integration Service generates a row error for any row that contains null characters in a string. Default is disabled. |
Line sequential buffer length | Number of bytes that the Data Integration Service reads for each line. This property, together with the total row size, determines whether the Data Integration Service drops a row. If the row exceeds the larger of the line sequential buffer length or the total row size, the Data Integration Service drops the row and writes it to the mapping log file. To determine the total row size, add the column precision and the delimiters, and then multiply the total by the maximum bytes for each character. Default is 1024. |
Generate Run-time Column Names | Determines how to generate the column metadata at run time. Select one of the following options:
|
Control file name | Name of the control file. Required if you generate run-time column names from control file. |
Control file directory | Directory where the control file exist. Required if you generate run-time column names from control file. |
Default Field Type | Data type of the additional ports generated at run time. |
Default Precision | Precision of the additional ports generated at run time. |
Default Scale | Scale of the additional ports generated at run time. |
Constraints | Conditional expression that the values on a data row must satisfy. Use the Expression editor to enter an expression that evaluates to TRUE. When the Data Integration Service reads constraints, it drops the rows that do not evaluate to TRUE. For example, a source flat file has an AGE column. You can set a constraint with AGE < 70 on the flat file data object. The Data Integration Service reads rows from the source flat file with the constraint AGE < 70. If the Data Integration Service reads rows with AGE >= 70, it drops those rows. |
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Append if exists | Appends the output data to the target files and reject files. If you do not select this option, the Data Integration Service truncates the target file and reject file before writing data to them. If the files do not exist, the Data Integration Service creates them. Default is disabled. |
Create directory if not exists | Creates the target directory if it does not exist. Default is disabled. |
Header options | Creates a header row in the file target. You can choose the following options:
Default is no header. |
Header command | Command used to generate the header row in the file target. |
Footer command | Command used to generate the footer row in the file target. |
Output type | Type of target for the mapping. Select File to write the target data to a flat file. Select Command to output data to a command. |
Command | Command used to process the target data. On UNIX, use any valid UNIX command or shell script. For example, use the following command to generate a compressed file from the target data on UNIX: compress -c - > MyTargetFiles/MyCompressedFile.Z On Windows, use any valid DOS command or batch file. The flat file writer sends the data to the command instead of a flat file target. For example, use cmd as the target command on Windows to avoid staging data in the file system and to avoid any security breaches. You can improve mapping performance by pushing transformation tasks to the command instead of the Data Integration Service. You can also use a command to sort or to compress target data. |
Merge command | Merge command used to process merge data for all target partitions. The Data Integration Service must use a concurrent merge type for a command to process merge data. The command might not maintain the order of the target data. |
Output file directory | Output directory for the flat file target. The machine that hosts Informatica services must be able to access this directory. Enter multiple directories separated by semicolons to increase performance when multiple partitions write to the flat file target. Default is the TargetDir system parameter. |
Output file name | File name of the flat file target. If multiple partitions write to the flat file target and you choose not to merge target data, each partition writes to a separate output file named <output_file_name><partition_number>.out. |
Merge type | Type of merge that the Data Integration Service performs on the data for partitioned targets. If the Data Integration Service does not create partitions for the target, it ignores this value. Select one of the following options:
|
Merge file directory | Directory for the merge file for all target partitions. The machine that hosts Informatica services must be able to access this directory. Default is the TargetDir system parameter. |
Merge file name | Name of the merge file for all target partitions. Default is the output file name. |
Connection type | The type of connection. Select from the following options:
Default is None. |