Bad Record Exception Mapping Example
An organization conducts a data project to review new customer data. The organization needs to verify that customer contact data is valid. The following example shows how to define a Bad Record Exception transformation that receives records from a mapplet that does a data quality analysis of customer records.
Create a mapplet with data quality transformations that evaluate the format and the accuracy of the customer data. The mapplet includes transformations that generate a record score based on the results of the data quality analysis. The transformations also define the quality issues for the data based on the results of the analysis.
Bad Record Exception Mapplet
Create a mapplet that contains data quality transformations to check the values of certain fields. The transformations check reference tables and content sets to determine if the fields in the records are valid. The transformations apply a record score to each record based on the results. The Exception transformation receives the records from the mapplet and routes each record to the appropriate output based on the record score.
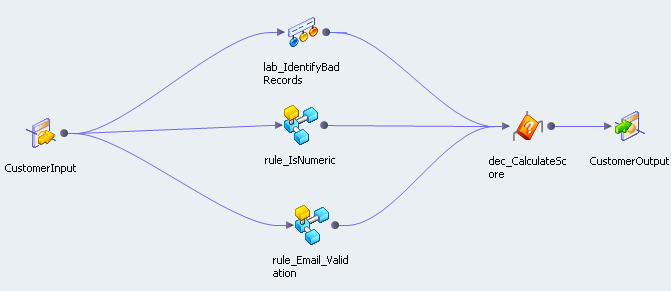
The mapplet consists of Labeler transformations, Decision transformations, and Expression transformations.
The following figure shows the objects in the mapplet:
The mapplet performs the following tasks:
- •A Labeler transformation verifies the locality, the state, the country code, the zip code, and the postal code data that it receives in the input ports. The transformation contains a strategy for each port. The strategies compares the source data to reference tables and identifies values that are not valid.
- •An Expression transformation mapplet verifies that the phone number is numeric and verifies that the number contains 10 digits.
- •A Labeler transformation and an Expression transformation mapplet verifies that the email address is valid. The Expression transformation verifies the structure of the email string. The Labeler transformation checks the IP address against a reference table of international IP address suffixes.
- •A Decision transformation receives the output from the transformation and the mapplets. It calculates an overall record score for the customer contact record.
Create a bad record exception mapping that includes the mapplet. The bad record exception mapping includes an Exception transformation that writes the exceptions to a bad records database table. A data analyst researches and updates exception records in the bad record table with the Analyst tool.
Bad Record Exception Example Input Groups
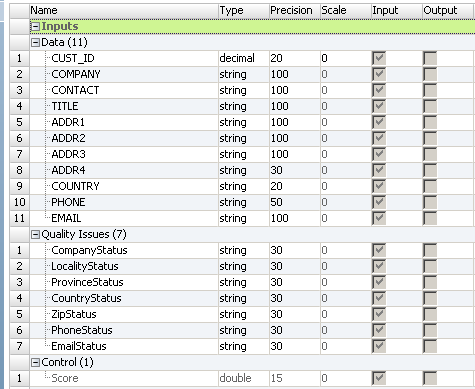
The Exception transformation has three input groups. The transformation has a Data group that receives the source data. It has the Quality Issues group, which receives data quality issues found by data quality transformations. It also has a Control group that contains the record score for the row.
The following figure shows the input groups in the Exception transformation:
Bad Record Exception Example Configuration
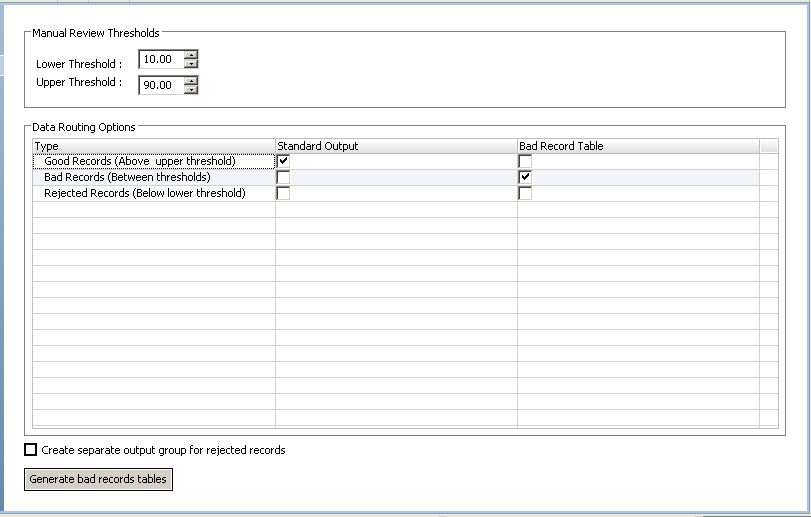
Define the upper and lower thresholds on the Configuration view. Identify where the transformation writes good records, bad records, and rejected records.
Accept the default configuration for routing the good records, bad records, and issues.
The following figure shows the Exception transformation Configuration view:
The following table describes the configuration settings:
Option | Setting |
|---|
Lower threshold | 10 |
Upper threshold | 90 |
Good records | Standard output |
Bad Records | Bad record table |
Rejected Records | - |
Click Generate bad records tables to create the Bad Records and Issues tables.
Bad Record Exception Example Mapping Output
Add a Write transformation to the mapping and connect the standard output ports to the data object. The mapping also contains the bad record database object and the issues database object you created on the Configuration view.
Bad Records Table
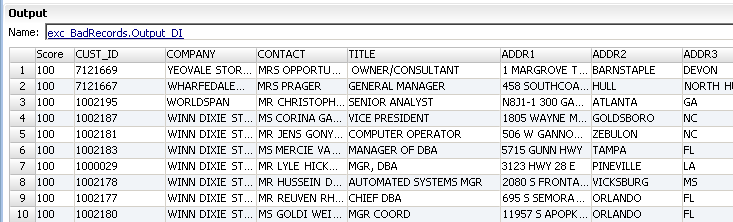
The Bad Records table contains the exceptions with record scores between the lower and upper thresholds.
The following figure shows the bad records that the Exception transformation returns:
The Bad Records table includes all of the fields in the source record. A bad record also includes the following fields:
- Workflow_ID
- The name of the workflow that included the Exception transformation. The workflow contains the Exception transformation Mapping task and the Human task to review the issues. The Workflow_ID contains DummyWorkflowID if the Exception transformation is not in a workflow .
- Row_Identifier
- A unique number that identifies each row.
- Record_Status
- A record status for the Analyst tool. Each record in the Bad Records table receives an Invalid status. You can maintain the record status when you update records in the Analyst tool.
Issues Table
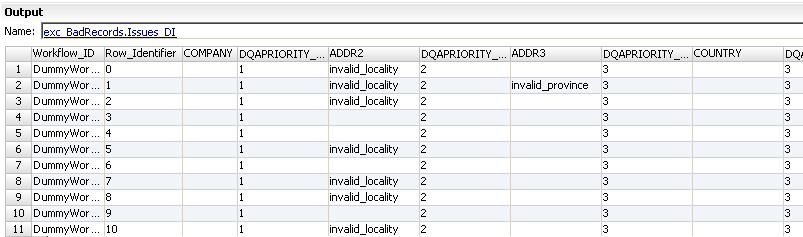
The Issues table contains one row for each row in the Bad Records table. Each row contains the issues that the data quality analysis found for the source record.
The following figure shows the columns in the Issues table:
The Issues table contains the following columns:
- Workflow_ID
- Identifies the workflow that created the record. The workflow contains the Exception transformation Mapping task and the Human task to review the issue.
- Row_Identifier
- Identifies the record row in the database table. The row identifier identifies which row in the Bad Records table corresponds to the row in the Issues table.
- Issue Field Name
- The field name is the name of the field that might quality issues. When the field contains an error the column value is the quality issue text. In the figure above, the ADDR2 field name contains the invalid_locality quality issue.
- DQAPriority
- The issue priority. When multiple issues occur for the same field, the issue with the highest priority appears in the Issue Field Name.
Good Records Table
Each record in the Good Records table has a record score greater than the upper threshold. In this example, the upper threshold is 90.
The following figure shows the good records that the Exception transformation returns:
The Good Records table records contain the record score and the source data fields.