Data Synchronization Example
You need to synchronize event data and venue data between a MySQL database and Amazon Redshift to create an event catalog. In MySQL, you have an event object and a venue object. You need to read from these related MySQL objects before writing to Amazon Redshift. For the initial data load, configure a data synchronization task to insert data to Amazon Redshift. For incremental updates, schedule a data synchronization task to upsert data to Amazon Redshift.
Create a JDBC connection to the MySQL database and create an Amazon Redshift connection. Configure a data synchronization task to use the insert operation.
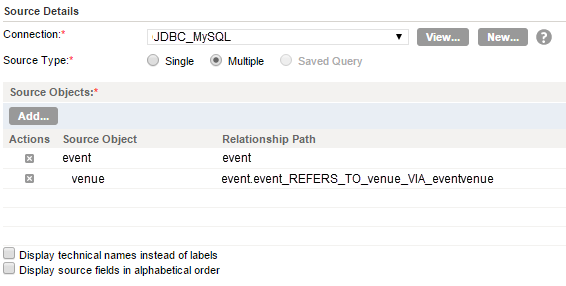
Select the MySQL objects you want to use, and the predefined relationship displays.
The following image shows the event object and the venue object added as source objects:
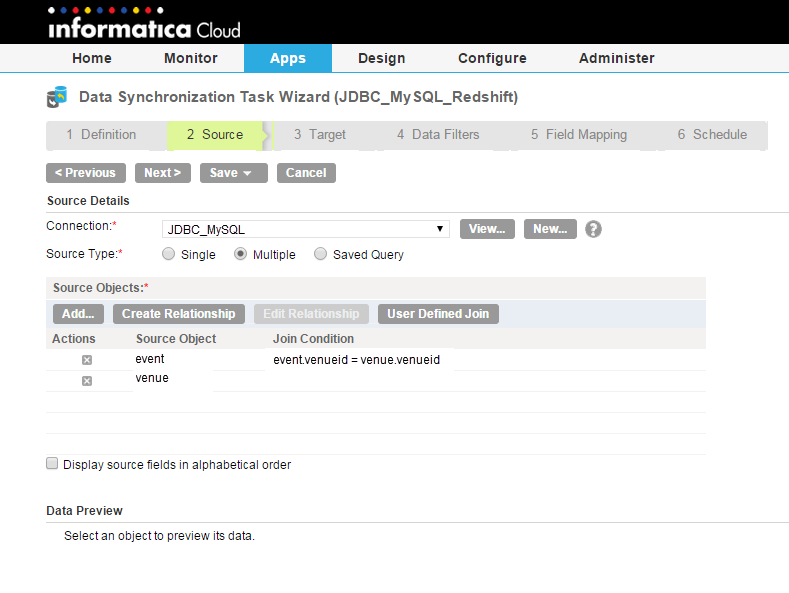
Save and run the task for the initial data load.
You can synchronize the data incrementally after the initial data migration. Create a data synchronization task that uses the upsert operation with the same MySQL source and the same Amazon Redshift target. To upsert data that has changed since the last data synchronization, configure a simple data filter that uses the $LastRunTime or $LastRunDate variable.
The following image shows a data filter that loads records when the last modified date is greater than the $LastRunTime system variable:
Save the task and configure it to run on a schedule so the data remains synchronized.