NetSuite Connector Administration
The administrator can perform the following tasks to ensure that NetSuite fields are available in Informatica Cloud and to optimize performance:
- • If field names in the NetSuite record and the related NetSuite search record do not match, the fields cannot be used in filters. This must be configured before NetSuite objects can be used as sources in tasks.
You can associate NetSuite record field names with related NetSuite search record field names when you set up a NetSuite connection in Informatica Cloud. Alternatively, you can configure the RecordToFieldsMap.ini file if the connection uses a Secure Agent group for the runtime environment.
- •Some custom fields in NetSuite custom objects might not appear in Informatica Cloud, particularly transaction body fields and transaction column fields.
To ensure that all custom fields are available in Informatica Cloud, you can configure custom fields when you set up a NetSuite connection in Informatica Cloud. Alternatively, you can configure the NetSuiteCustomFields.ini file if the connection uses a Secure Agent group for the runtime environment.
- •Saved search fields in NetSuite do not appear in Informatica Cloud if they have a null value.
You can specify saved search fields when you configure a NetSuite connection so that the saved search fields appear in Informatica Cloud even when they have a null value. Alternatively, you can add the saved search fields to the NetSuiteSavedSearchFields.ini file if the connection uses a Secure Agent group for the runtime environment.
- •To optimize performance for concurrent threads in Data Synchronization tasks, you might need to adjust heap size.
Mapping NetSuite Record Field Names
Map NetSuite record field names with related NetSuite search record field names so that users can use the fields in filters.
Users define filters for fields in the following locations:
- •Data Filters page of the Data Synchronization Task wizard
- •Query options in a Source transformation in the Mapping Designer
- •Query options in the Sources page of the Mapping Configuration Task wizard when the source object is parameterized
NetSuite SearchBasic search records contain the field names used for filtering. When a field name in a NetSuite record matches the related field name in the corresponding SearchBasic search record, users can define a filter for the field in tasks. When a field name in a record does not match the related search record field name, users cannot define a filter for the field in tasks.
You can check the NetSuite schema to see if a field name in a NetSuite record matches the related field name in the SearchBasic search record. NetSuite records are represented as schema types in the NetSuite schema. To view NetSuite field names in the NetSuite schema, you can open the appropriate schema definition file (XSD). You can find a list of XSDs in the following location:
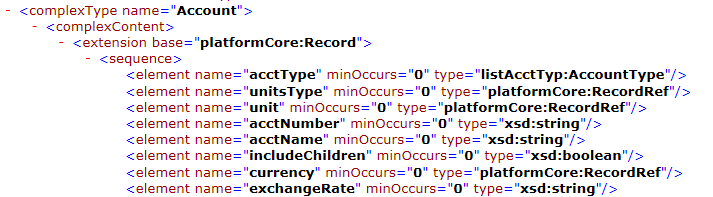
For example, a user wants to define a filter for account name. You review the Account record in NetSuite's browser, which is defined in NetSuite's accounting.xsd file.
The schema contains the field, acctName, as shown in the following sample:
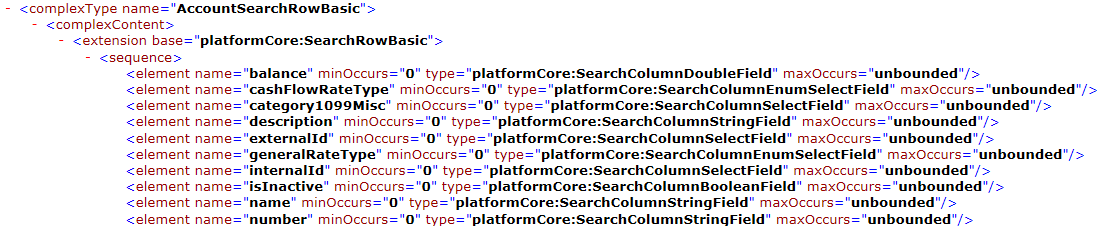
You also see that the corresponding SearchBasic field name in the NetSuite's common.xsd file is called name, as shown in the following sample:
Because the field name is acctName in the Account record and the field name is name in the corresponding SearchBasic record, you map the two field names. The following example shows how you map acctName to name in the connection properties:
[Account]
acctName=name
Use the same syntax if you resolve the issue in the RecordToFieldsMap.ini file.
Creating a Configuration File to Map NetSuite Fields
To ensure that users can define filters for NetSuite fields, map record field names with related NetSuite search record field names. You can map the fields in the Record Filter Fields connection property when you configure a NetSuite connection. Alternatively, if the NetSuite connection uses a Secure Agent group as the runtime environment, you can create a configuration file to map the fields.
If you choose to create a configuration file to map the fields, perform the following steps:
1. Create a text file named RecordToFieldsMap.ini.
2. Use the following guidelines to configure the RecordToFieldsMap.ini file:
- - Create a separate section for each NetSuite record.
- - In each section, list the record field names and related SearchBasic field names, as follows:
[<record 1>]
<record field name>=<SearchBasic field name>
<record field name2>=<SearchBasic field name2>
[<record 2>]
<record field name>=<SearchBasic field name>
<record field name2>=<SearchBasic field name2>
<record field name3>=<SearchBasic field name3>
For example:
[Account]
acctName=name
addr1=address1
- - To read transactional data from NetSuite when memorized transaction is enabled in the NetSuite account, add the record field names and related SearchBasic field name in the following format:
[<record 1>]
<record field name>=<SearchBasic field name>
For example:
If you want to enable memorized transaction for JournalEntry object, add the following value in the RecordToFieldsMap.ini file:
[JournalEntry]
reversalEntry=memorized
3. Copy the RecordToFieldsMap.ini file to the following directory:
<Secure Agent installation directory>\apps\Data_Integration_Server\ext\deploy_to_main\bin\rdtm-extra\reserved\userfiles\netsuite
4. Update the file as required.
Configuring the NetSuiteCustomFields.ini File
You can specify custom NetSuite fields in the Record Custom Fields connection property when you configure a NetSuite connection so that the fields are available in Informatica Cloud. Alternatively, if the NetSuite connection uses a Secure Agent group as the runtime environment, you can specify the custom NetSuite fields in the NetSuiteCustomFields.ini file.
If you choose to configure the NetSuiteCustomFields.ini file, perform the following steps:
1. Make a copy of the NetSuiteCustomFields.ini file, located in the following directory:
<Secure Agent installation directory>\downloads\packageNetsuiteConnector.<version>\package\rdtm\javalib
2. Use the following guidelines to change the file to include custom NetSuite fields:
- - Create a separate section for each NetSuite record for which you want to add custom fields.
- - Add the custom fields using the following format, where the value of scriptId is the ID field in the NetSuite user interface for each custom field:
[<Object Name>]
scriptIds = <custom field name1>,<custom field name2>,<custom field name3>
For example:
[Sales]
scriptIds = discountPrice,salesDescription,salesEvent
- - Add the custom fields for NetSuite advanced search using the following format, where the value of scriptId is the ID field in the NetSuite user interface for each custom field:
[<Object Name>]
scriptIds = <custom field name1>,<custom field name2>,<custom field name3>
For example:
[EmployeeSearchAdvanced]
scriptIds = custentity74,custentity66
- - If you want to read or write custom segment data, use the following format to add the custom segment fields:
[<Object Name>]
custSegScriptIds=custseg1:select,custseg2:multiselect,custseg3:select....
where the value of scriptId is the ID field in the NetSuite user interface for each custom segment field.
For example:
[Employee]
custSegScriptIds=custbody18:select,custbody19:multiselect,custbody20:select....
If you want to read data from or write data to child record custom segments, use the following format to add the child custom segment fields:
[<Object Name>]
custSegScriptIds=custseg1:select,custseg2:multiselect,custseg3:select....
For example:
▪ [JournalEntry] custSegScriptIds=custbody_cseg1:select,custbody_cseg2:select,custbody_cseg3:select
▪ [JournalEntryLineList] custSegScriptIds=custcol_cseg1:select,custcol_cseg2:select,custcol_cseg3:select
3. Save the NetSuiteCustomFields.ini in the following location:
<Secure Agent installation directory>\apps\Data_Integration_Server\ext\deploy_to_main\bin\rdtm-extra\reserved\userfiles\netsuite
Note: The custom segment fields, which you add either in NetSuiteCustomFields.ini or connection properties, are not validated. For example, the metadata and duplicate field names.
Configuring the NetSuiteSavedSearchFields.ini File
You can specify saved search fields in the Saved Search Record Fields connection property when you configure a NetSuite connection to ensure that all saved search fields are available in Informatica Cloud. Alternatively, if the NetSuite connection uses a Secure Agent group as the runtime environment, you can configure the NetSuiteSavedSearchFields.ini file.
If you choose to configure the NetSuiteSavedSearchFields.ini file, perform the following steps:
1. Make a copy of the NetSuiteSavedSearchFields.ini file, located in the following directory:
<Secure Agent installation directory>\downloads\packageNetsuiteConnector.<version>\package\rdtm\javalib
2. Use the following guidelines to change the file to include all of the saved search fields:
- - Create a separate section for each NetSuite saved search record for which you want to add a saved search field, identified by a unique scriptId.
- - Add the search fields using the following format:
[SavedSearchScriptIdToFieldsMap<version>]
<savedSearchId1>=<savedSearchDeclaredField1Name>,<savedSearchDeclaredField2Name>,
<savedSearchCustomFieldScriptId1>,<savedSearchCustomFieldScriptId2>,<StandardJoin>|<FieldName1>,
customSearchJoin|<scriptID1>
The savedSearchId1 is ID field in the NetSuite user interface that specify the saved search record. The savedSearchDeclaredField1Name and savedSearchDeclaredField2Name are standard field names in the NetSuite user interface. The savedSearchCustomFieldScriptId1 and savedSearchCustomFieldScriptId2 are ID fields in the NetSuite user interface for custom fields. The StandardJoin|FieldName1 is the standard join field and customSearchJoin|scriptID1 is the custom join field.
For example:
[SavedSearchScriptIdToFieldsMap1]
1000=phone,email,custentity78,custentity65,userJoin|email,customSearchJoin|custrecord1424
In the example, 1000 is the saved Search ID, phone and email are standard field names, custentity78 and custentity65 are the script IDs of a custom field. userJoin|email is the standard join field and customSearchJoin|custrecord1424 is the custom join field script ID.
Note: When you use custom join, script ID appears in the Informatica Cloud user interface.
- - If you want to read custom segment data, use the following format to add the search custom segment fields:
[SavedSearchScriptIdToCustSegFieldsMap]
savedSearchId1 = custseg1:select,custseg2:multiselect,custseg3:select....
where custom segment field scriptId is appended to field type (select or multiselect) with ":" delimiter.
For example:
[SavedSearchScriptIdToCustSegFieldsMap]
741=custseg1:select,custentity_cseg1:select,custentity_csegcs_multsel:multiselect
3. Save the NetSuiteSavedSearchFields.ini in the following location:
<Secure Agent installation directory>\apps\Data_Integration_Server\ext\deploy_to_main\bin\rdtm-extra\reserved\userfiles\netsuite
Fetching Field Name for Saved Search with Standard Join
Perform the following steps to fetch field name for standard join:
2. Under Schema Browser, select the object.
3. Under Related Searches, select the search object.
4. Under Fields, select the type for the standard join.
You will find the name of the standard join field.
The syntax for saved search INI file with standard join is as follows,
[SavedSearchScriptIdToFieldsMap]<savedSearchId1>= <StandardJoin>|<FieldName1>, <StandardJoin>|<FieldName2>
For example,
[SavedSearchScriptIdToFieldsMap1]
290= userjoin|accountNumber, contactJoin|address
Fetching Script ID for Saved Search with Custom Join
Perform the following steps to fetch script ID for custom join:
1. Log in to your NetSuite account.
2. Select Customization > Record Types.
3. Select the custom object to get the script ID for the custom join field.
The syntax for saved search INI file with custom join is as follows:
[SavedSearchScriptIdToFieldsMap]<savedSearchId1>= customSearchJoin|<scriptID1>,customSearchJoin|<scriptID2>
For example,
[SavedSearchScriptIdToFieldsMap1]
290= customSearchJoin|custrecord1423,customSearchJoin|custrecord1421
Reading Custom Record Standard Fields with Custom Join
To read custom record standard fields with custom join, configure the DumpSavedSearchMetadata property.
1. Click Configure > Runtime Environments.
The Runtime Environments page appears.
2. Select the Secure Agent for which you want to set the custom configuration flag.
3. Click Edit Secure Agent icon corresponding to the Secure Agent you want to edit.
The Edit Secure Agent page appears.
4. Select the Service as Data Integration Server in the Custom Configuration Details section.
5. Select the Type as Tomcat in the Custom Configuration Details section.
6. Add DumpSavedSearchMetadata in the Name field.
7. Specify a file path in the Value field where you want to generate the DumpSavedSearchMetadata file.
For example, C:\\Dump.txt. The path should contain "\\".
The following image shows the Custom Configuration Details section.
Note: If the path contains only the file name, then the Secure Agent generates the DumpSavedSearchMetadata file in the following folder: <Secure Agent installation directory>\apps\Data_Integration_Server\<DIS Version>\ICS\main\tomcat. If the path is not valid, the Secure Agent does not generate the DumpSavedSearchMetadata file.
8. Click OK.
9. Create a task with saved search object to read custom record standard fields with custom join.
When you save or run the task, the Secure Agent generates the DumpSavedSearchMetadata file and writes the metadata to this file. The Secure Agent fetches the metadata for the custom record standard fields in the following format:
<script Id of custom record>__<standard search column name1>__CSJ,
<script Id of custom record>__<standard search column name2>__CSJ
For example:
custbody_cseg1__internalId__CSJ,custbody_cseg1__name__CSJ
Note: When you specify a field name, ensure that the length of the field name does not exceed 64 characters.
If you want to override the metadata, you can copy the metadata in the NetSuiteSavedSearchFields.ini file and modify the metadata accordingly. Use the following format to add the search custom record standard fields in the NetSuiteSavedSearchFields.ini file:
[SavedSearchScriptIdToFieldsMap<version>]
<savedSearchId1>=CustomSearchJoin|<scriptId of custom record>__<standard field name>
For example:
[SavedSearchScriptIdToFieldsMap1]
356=CustomSearchJoin|uss_custom_code__internalId
Alternatively, you can specify saved search fields in the Saved Search Record Fields connection property when you configure a NetSuite connection.
Internalid and Externalid in Saved Search
When you create a new task or edit or refresh an existing task to read data from NetSuite saved search that contains an internalid or externalid field, the agent does not drill down the internalid or externalid field if you do not specify the saved search fields in the NetSuiteSavedSearchFields.ini file or Saved Search Record Fields connection property. The agent writes the internalid field as internalid and externalid field as externalid.
If you specify the saved search fields in the NetSuiteSavedSearchFields.ini file or Saved Search Record Fields connection property, the agent drills down the internalid or externalid field. The agent drills down the internalid field as internalid_internalid, internalid_externalid, internalid_type, and internalid_name. The agent drills down the externalid field as externalid_externalid, externalid_internalid, externalid_type, and externalid_name.
Note: If you edit or refresh an existing task, you must remap the internalid or externalid field or create a new target file.
Increasing Heap Size for Concurrency in Data Synchronization Tasks
Users can configure Data Synchronization tasks to use concurrent threads. If the NetSuite connection for Data Synchronization tasks uses a Secure Agent group as the runtime environment, you can adjust heap size to optimize performance for concurrency.
You can adjust heap size in the Edit Secure Agent page or you can edit the pmrdtm configuration file.
Increasing Heap Size in the Edit Secure Agent Page
You can adjust heap size in the Edit Secure Agent page to optimize performance for concurrency.
1. Click Configure > Runtime Environments.
2. On the Runtime Environments page, if necessary, expand the Secure Agent groups to see the list of Secure Agents. Click the Secure Agent name from the list.
3. Click Edit on the View Secure Agents page.
4. In the System Configuration Details section, for Type, select DTM. Modify the JVMOption parameter to specify the heap size.
For example, you might want to adjust the heap size to 512 MB if the concurrency thread setting is 10.
The following example shows the heap size set to 512 MB:
JVMOption6=-Xmx512m
JVMOption5=-XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError
JVMOption4=-Xloggc:jvm_heap_stats_Clou_App.log
JVMOption3=-XX:+PrintGCDetails
JVMOption2=-XX:+PrintGCTimeStamps
JVMOption1=-verbose:gc
Handling Parent and Child or Sibling Objects with Similar Column Name
If the parent object and the child or sibling object have similar column names, data from parent column is written to the parent column, and data from child or sibling column is written to the child or sibling column. You can set the UseJumbledDataForFieldsWithSameName property to control this behavior.
If you set the UseJumbledDataForFieldsWithSameName property to true, data from parent column is written to the child or sibling column, and data from child or sibling column is written to the parent column.
If you set the UseJumbledDataForFieldsWithSameName property to false, data from parent column is written to the parent column, and data from child or sibling column is written to the child or sibling column.
1. Click Configure > Runtime Environments.
2. On the Runtime Environments page, if necessary, expand the Secure Agent groups to see the list of Secure Agents. Click the Secure Agent name from the list.
3. Click Edit on the View Secure Agents page.
4. In the Custom Configuration Details section, for Type, select DTM.
5. Set the UseJumbledDataForFieldsWithSameName parameter to true or false as shown in the following image:
6. Restart the Secure Agent.