ODBC Sources in Mappings
In a mapping, you can configure a Source transformation to represent a single ODBC source, multiple ODBC sources, ODBC query or ODBC parameter.
The following table describes the ODBC source properties that you can configure in a source transformation:
Property | Description |
|---|
Connection | Name of the source connection. |
Source Type | Type of source object. Select Single Object, Multiple Objects, Query or Parameter. |
Object | Name of the source object. Select the source object for the task. |
Objects and Relationships | Adds multiple objects. Click on Add Source Object. Note: The Objects and Relationships property appears only if you select Multiple Objects as the source type. |
Query | Click on Define Query and enter a valid custom query. Note: The Query property appears only if you select Query as the source type. |
Parameter | The parameter for the source object. Create or select the parameter for the source object. Note: The parameter property appears only if you select Parameter as the source type. |
Filter | Filters records and reduces the number of rows that the Secure Agent reads from the source. Add conditions in a read operation to filter records from the source. |
Sort | Sorts records based on the conditions you specify. |
Select distinct rows only | Eliminates duplicate rows. Select one of the following options: - - True. Eliminates duplicate rows before inserting new rows.
- - False. Inserts new rows without eliminating duplicate rows.
|
Tracing Level | Sets the amount of detail that appears in the log file. Select Normal, Verbose Initialization or Verbose Data. Default is normal. |
Pre SQL | Executes SQL query before loading records to the database. For example, if you want to delete the records from database before the latest records load, write a Pre SQL. |
Post SQL | Executes SQL query after loading records to the database. |
Output is Deterministic | Specify only when the source output does not change between session runs. |
Output is Repeatable | Specify only when the order of the source output is same between the session runs. Select Never or Always. |
Key Range Partitioning
You can configure key range partitioning when you use a Mapping Configuration task to read data from ODBC sources. With key range partitioning, the Secure Agent distributes rows of source data based on the field that you define as partition keys. The Secure Agent compares the field value to the range values for each partition and sends rows to the appropriate partitions.
Use key range partitioning for columns that have an even distribution of data values. Otherwise, the partitions might have unequal size. For example, a column might have 10 rows between key values 1 and 1000 and the column might have 999 rows between key values 1001 and 2000. If the mapping includes multiple sources, use the same number of key ranges for each source.
When you define key range partitioning for a column, the Secure Agent reads the rows that are within the specified partition range. For example, if you configure two partitions for a column with the ranges as 10 through 20 and 30 through 40, the Secure Agent does not read the rows 20 through 30 because these rows are not within the specified partition range.
You can configure a partition key for fields of the following data types:
- •String
- •Any type of number data type. However, you cannot use decimals in key range values.
- •Date/time type. Use the following format: MM/DD/YYYY HH24:MI:SS
You cannot use key range partitions when a mapping includes any of the following transformations:
- •Web Services
- •XML to Relational
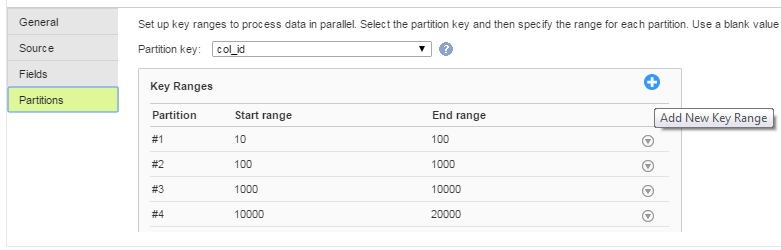
Configure Key Range Partitioning
Perform the following steps to configure key range partitioning for ODBC sources:
1. In the Source Properties, click the Partitions tab.
2. Select the required partition key from the list.
3. Click Add New Key Range to define the number of partitions and the key ranges based on which the Secure Agent must partition data.
Use a blank value for the start range to indicate the minimum value. Use a blank value for the end range to indicate the maximum value.
The following image displays the
Partitions tab: