Unconnected Lookups
An unconnected Lookup transformation is a Lookup transformation that is not connected to other transformations in a mapping. A transformation in the mapping pipeline calls the Lookup transformation with a :LKP expression. The unconnected Lookup transformation returns one column to the calling transformation.
Note: You can use an unconnected lookup only with a database or flat file data source.
The following table lists the differences between connected and unconnected Lookup transformations:
Functionality | Connected Lookup | Unconnected Lookup |
|---|
Input values | Receives input values directly from the mapping pipeline. | Receives input values from the result of a :LKP expression in another transformation. |
Cache | Cache includes all lookup columns used in the mapping. This includes columns in the lookup condition and columns linked as output fields to other transformations. | Cache includes all lookup/output fields in the lookup condition and the lookup/return field. |
Return values | Returns multiple values from the same row. | Returns the specified field for each row. |
Lookup conditions | If there is no match for a lookup condition, Informatica Cloud returns the default value for all output fields. If there is a match, Informatica Cloud returns the results of the lookup condition for all lookup/output fields. | If there is no match for the lookup condition, Informatica Cloud returns NULL. If there is a match, Informatica Cloud returns the result of the lookup condition to the return field. |
Output values | Passes multiple output values to another transformation. Links lookup/output fields to another transformation. | Passes one output value to another transformation. The lookup/output/return field passes the value to the transformation that contains the :LKP expression. |
User-defined values | Supported | Not supported |
Configuring an Unconnected Lookup Transformation
To configure an unconnected Lookup transformation, select the Unconnected Lookup option, add incoming fields, configure the lookup condition, and designate a return value. Then configure a lookup expression in a different transformation.
1. On the General tab of the Lookup transformation, enable the Unconnected Lookup option.
2. Create the incoming fields.
On the Incoming Fields tab of the Lookup transformation, create an incoming field for each argument in the :LKP expression. For each lookup condition you plan to create, you need to add an incoming field to the Lookup transformation. You can create a different field for each condition, or use the same incoming field in more than one condition.
3. Designate a return value.
You can pass multiple input values into a Lookup transformation and return one column of data. Informatica Cloud can return one value from the lookup query. Use the return field to specify the return value.
4. Configure a lookup expression in another transformation.
Supply input values for an unconnected Lookup transformation from a :LKP expression in a transformation that uses expressions such as an Expression, Aggregator, Filter, or Router transformation. The arguments are local input fields that match the Lookup transformation input fields used in the lookup condition.
Calling an Unconnected Lookup from Another Transformation
Supply input values for an unconnected Lookup transformation from a :LKP expression in another transformation such as an Expression transformation or Aggregator transformation. You can call the same lookup multiple times in one mapping.
Use the following syntax for a :LKP expression:
:LKP.<Lookup transformation name> (<argument>, <argument>, ...)
The arguments are local input fields that match the Lookup transformation input fields used in the lookup condition.
For example, the following expression passes the ITEM_ID and PRICE fields to an unconnected Lookup transformation named lkp_ItemPrices:
:LKP.lkp_ItemPrices (ITEM_ID, PRICE)
Use the following guidelines to write an expression that calls an unconnected Lookup transformation:
- •The order in which you list each argument must match the order of the lookup conditions in the Lookup transformation.
- •The datatypes for the fields in the expression must match the datatypes for the input fields in the Lookup transformation.
- •The argument fields in the expression must be in the same order as the input fields in the lookup condition.
- •If you call a connected Lookup transformation in a :LKP expression, Informatica Cloud marks the mapping invalid.
Unconnected Lookup Example
You can use an unconnected Lookup transformation to replace cryptic or numeric ID values in a table with meaningful names from a lookup table.
For example, you need to load some sales order data from SAP transactional tables to a relational table in your data warehouse. The SAP tables contain numeric IDs for values such as the sales group and sales office. In the data warehouse table, you want to replace the numeric IDs with the corresponding names in your local language. The name that is associated with each ID is stored in a reference table. Use an unconnected Lookup transformation to retrieve the names from the reference table.
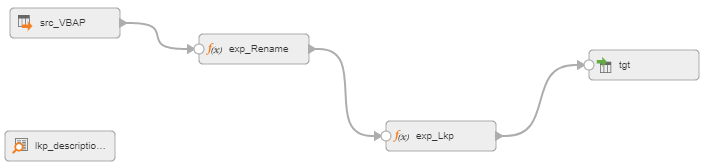
The following image shows the mapping:
Configure the transformations in the following ways:
- Source transformation
Use a Source transformation to specify the tables from which to extract data.
On the Source tab, configure the source connection and select the tables from which you want to extract data.
- First Expression transformation (optional)
Optionally, use an Expression transformation to rename fields and replace null values.
On the Incoming Fields tab, use the Named Fields field selection criteria to select the fields that you want to load to the target table. If required, rename the selected fields to give them more meaningful names.
On the Expression tab, create output fields to replace the null values. For example, to replace null values for the sales group code and sales office code with spaces, you might create the following output fields:
Output Field | Expression |
|---|
in_sales_group | IIF(ISNULL(sales_group_code),' ',sales_group_code) |
in_sales_office | IIF(ISNULL(sales_office_code),' ',sales_office_code) |
- Unconnected Lookup transformation
Use an unconnected Lookup transformation to retrieve the descriptions from the reference table.
On the General tab, enable the Unconnected Lookup option.
On the Incoming Fields tab, create an incoming field for each value that you need to pass to the Lookup transformation to retrieve the data that you want. For example, to pass the domain name, language, and code value to the Lookup transformation, create the in_domain_name, in_language, and in_lookup_code fields.
On the Lookup Object tab, configure the lookup connection and select the reference table that you want to use as the lookup table.
On the Lookup Condition tab, specify the lookup condition for each incoming field. For example:
Lookup Field | Operator | Incoming Field |
|---|
domain_name | = | in_domain_name |
language_code | = | in_language |
lookup_code | = | in_lookup_code |
On the Return Fields tab, select the field in the reference table that you want to return. For example, to return a description, you might select lookup_description as the return field.
- Second Expression transformation
Use an Expression transformation to call the unconnected Lookup transformation and retrieve the name that is associated with each ID value.
On the Incoming Fields tab, include all fields from the upstream transformation.
On the Expression tab, create an output field to retrieve each description from the Lookup transformation. Call the Lookup transformation with a :LKP expression. For example, to retrieve the sales group and sales office names from the appropriate domain in English, you might create the following output fields:
Output Field | Expression |
|---|
sales_group | :LKP.lkp_Descriptions('sales_group','en',in_sales_group) |
sales_office | :LKP.lkp_Descriptions('sales_office','en',in_sales_office) |
- Target transformation
On the Target tab, configure the target connection and select the relational table to which you want to load data.
On the Field Mapping tab, map the output fields from the upstream transformation to the appropriate target fields. For example, to map the sales_group and sales_office output fields from the second Expression transformation to the SALES_GROUP and SALES_OFFICE target fields, configure the following field mapping:
Target Field | Mapped Field |
|---|
SALES_GROUP | sales_group |
SALES_OFFICE | sales_office |