Substitution Masking
Substitution masking replaces a column of data with similar but unrelated data from a dictionary file.
The Data Masking task provides dictionaries that contain sample data for substitution masking. You can also use custom dictionaries. When you configure substitution masking, select the type of dictionary that contains the substitute values. The Data Masking task performs a lookup on the dictionary that you choose and replaces source data with data from the dictionary.
You can substitute data with repeatable or non-repeatable values. When you choose repeatable values, you must configure a seed value to substitute data with deterministic results.
Substitution Masking with Custom Dictionaries
Create and use custom dictionaries when you perform substitution masking.
You create and add a flat file dictionary to the Data Masking task. Add a connection to the flat file dictionary from the Configure | Connections view.
When you configure a data masking task, you can use the flat file dictionary connection to perform substitution masking. You cannot use a relational dictionary.
To support non-English characters, you can use different code pages from a flat file connection when you configure a substitution rule with custom dictionaries.
Substitution Masking Parameters
To perform substitution masking, you can select the custom dictionaries that you create or the dictionaries that the Data Masking application provides.
The following table describes the parameters that you can configure for substitution masking:
Parameter | Description |
|---|
Dictionary File | Appears if you select Custom Substitution from the list of masking rules. Click Select and specify the following parameters: - Flat File Connection
- The connection to the directory where the custom dictionaries are present. You must create a flat file connection with the directory that points to the dictionary files.
- Dictionary File
- The custom dictionary that you want to select. The dictionary file must be present for all the Secure Agents in a runtime environment in the following location:
<Secure Agent installation directory>\apps\Data_Integration_Server\data
|
Dictionary Column | The output column from the custom dictionary. Appears if you select Custom Substitution from the list of masking rules. You can select a dictionary column if the flat file contains column headers. |
Lookup Input Port | Optional. The source input column based on which you perform a lookup operation on the dictionary. |
Lookup Output Port | Optional. The dictionary column that you can look up based on the input port. |
Lookup Error Constant | Optional. A constant value that you can configure when there are no matching values for the lookup condition from the dictionary. |
Repeatable | Returns the same masked value when you run a task multiple times or when you generate masked values for a field that is in multiple tables. |
Seed Value | A starting number to create repeatable output. Enter a number from 1 through 999. Default seed value is 190. |
Custom Substitution Lookup Example
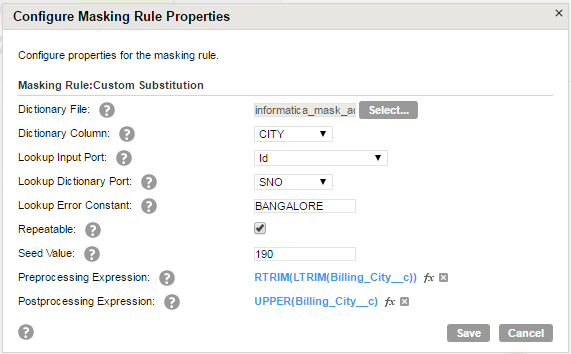
Consider that you apply substitution masking on the S_City column and you select a dictionary file with city names, identification numbers, and serial numbers. Select CITY as the dictionary column. The lookup input port is Id and the lookup dictionary port is SNO. If there are no matching values between the Id and SNO columns, the task uses the error constant BANGALORE as the lookup value.
The following image shows the substitution parameters for masking with custom dictionaries:
Custom Substitution Dictionary Lookup Use Cases
The task performs dictionary lookup in custom substitution masking in the following cases:
- •Case 1. If there are valid target lookup records in a dictionary for all the corresponding source records, the task picks all the values from the dictionary and replaces in the target.
- •Case 2. If there are some records in the source for which there are multiple lookup values in a dictionary, the task picks one of the lookup values from the dictionary and substitutes with the source value.
- •Case 3. if some of the source values are same as the lookup values in a dictionary, the target contains the same data as the source.
- •Case 4. If the source records do not have a lookup value in a dictionary and if you specify a valid error constant, the task uses the error constant for all the failed lookup conditions.
- •Case 5. If the source records do not have a lookup value in a dictionary and if you do not specify a valid error constant, the task fails and generates an exception.