Microsoft Azure Data Lake Store
Microsoft Azure Data Lake is a scalable data storage and analytics service. The service is hosted on Azure. Configure an Azure Data Lake Store (ADLS) resource type to extract metadata from the data lake store.
When you create a Azure Data Lake Store resource, you can access the files and folders in the following Azure storage products:
- Azure Data Lake Store or Data Lake Storage Gen1
- To access this repository, Enterprise Data Catalog uses service-to-service or OAuth 2.0 authentication. To use the OAuth 2.0 authentication, you must create an Azure Active Directory (AD) application, and use the client ID and client key from the application for authentication. Enterprise Data Catalog uses SDK to access the repository contents.
- Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2
- Azure Blob storage supports Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2. This is a hierarchical file system. When you create a Azure Data Lake Store resource and choose the Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 option, you need to enter the user account ID and one of the keys provided in the Access keys section. In the Azure portal, you can view the two keys that are generated for each Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 storage account in the Settings > Access keys section. To access the files and folders in this hierarchal file system, Enterprise Data Catalog uses REST APIs. Azure uses Shared Key authorization to authenticate the requests. In Enterprise Data Catalog, access and runtime is two times faster for Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 as compared to Data Lake Storage Gen1 storage.
Objects Extracted
Permissions to Configure the Resource
If you create a new user, ensure that you configure read permission on the data source for the new user account.
Supported File Types
The Microsoft Azure Data Lake Store resource enables you to extract metadata from structured and unstructured files.
The structured files supported are:
- •AVRO files
- •Delimited files
- •Text files
- •JSON files
- •Parquet files
- •XML files
The unstructured files supported are:
- •Apple files
- •Compressed files
- •Email
- •Microsoft Excel
- •Microsoft PowerPoint
- •Microsoft Word
- •Open Office files
- •PDF
- •Web page
- •Extended unstructured formats
Assign read and write permissions to the files to extract metadata.
Prerequisites
Before you create the resource, ensure that you have met the following prerequisites:
- 1. Merge the certificates in <INFA_HOME>/java/jre/lib/security/cacerts to <INFA_HOME>/services/shared/security/ infa_truststore.jks file.
- 2. Move the infa_truststore.jks file to a common location accessible to all the nodes in the cluster.
- 3. In the HDFS configuration properties of the Ambari interface, update the infa_truststore.jks file path in the ssl.client.truststore.location property and update the infa_truststore.jks password in the ssl.client.truststore.password property.
- 4. If the cluster is an embedded Hadoop cluster, restart the Informatica Cluster Service.
Note: Ensure that you configure the required permissions for the ADLS storage in Azure Active Directory.
Resource Connection Properties
The General tab includes the following properties:
Property | Description |
|---|
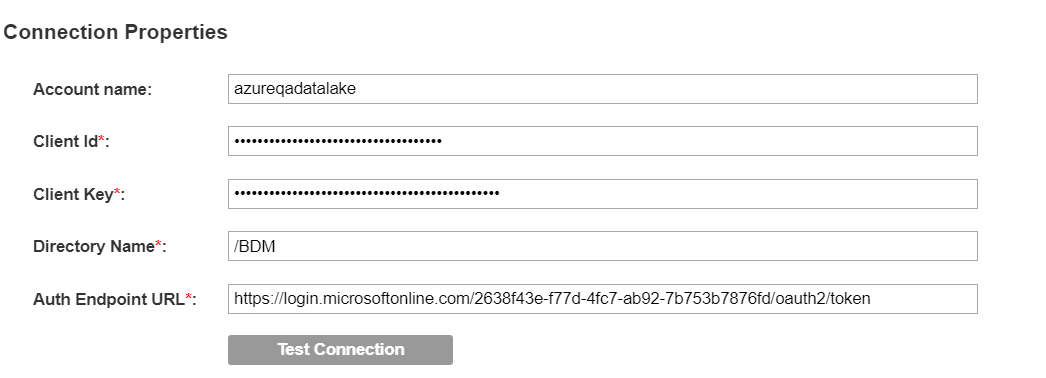
Account Name | Enter the storage account name that you created in the Azure portal. |
ADLS Source Type | Choose Data Lake Store Gen 1 or Data Lake Store Gen 2 option. |
Client Id | Enter the client ID to connect to the Microsoft Azure Data Lake Store. Use the value listed for the application ID in the Azure portal. This option appears when you choose the Data Lake Store Gen 1 option as the ADLS Source Type. |
Client Key | Enter the client key to connect to the Microsoft Azure Data Lake Store. Use the Azure Active Directory application key value in the Azure portal as the client key. This option appears when you choose the Data Lake Store Gen 1 option as the ADLS Source Type. |
Directory Name | Directory name of the Azure Data Lake Store. |
Auth EndPoint URL | The OAuth 2.0 token endpoint URL in the Azure portal. This option appears when you choose the Data Lake Store Gen 1 option as the ADLS Source Type. |
Storage Account Key | Enter key1 or key2 as the storage account key. Navigate to the Settings > Access keys section in Azure portal to view the storage account keys. This option appears when you choose the Data Lake Store Gen 2 option as the ADLS Source Type. |
The following image shows sample connection properties on the General tab:
The Metadata Load Settings tab includes the following properties:
Property | Description |
|---|
Enable Source Metadata | Extracts metadata from the data source. |
File Types | Select any or all of the following file types from which you want to extract metadata: - - All. Use this option to specify if you want to extract metadata from all file types.
- - Select. Use this option to specify that you want to extract metadata from specific file types. Perform the following steps to specify the file types:
- 1. Click Select. The Select Specific File Types dialog box appears.
- 2. Select the required files from the following options:
- - Extended unstructured formats. Use this option to extract metadata from file types such as audio files, video files, image files, and ebooks.
- - Structured file types. Use this option to extract metadata from file types, such as Avro, Parquet, JSON, XML, text, and delimited files.
- - Unstructured file types. Use this option to extract metadata from file types such as Microsoft Excel, Microsoft PowerPoint, Microsoft Word, web pages, compressed files, emails, and PDF.
- 3. Click Select.
Note: You can select Specific File Types option in the dialog box to select files under all the categories.
|
Other File Types | Extract basic file metadata such as, file size, path, and time stamp, from file types not present in the File Types property. |
Treat Files Without Extension As | Select one of the following options to identify files without an extension: |
Enter File Delimiter | Specify the file delimiter if the file from which you extract metadata uses a delimiter other than the following list of delimiters: - - Comma (,)
- - Horizontal tab (\t)
- - Semicolon (;)
- - Colon (:)
- - Pipe symbol (|)
Verify that you enclose the delimiter in single quotes. For example, '$'. Use a comma to separate multiple delimiters. For example, '$','%','&' |
First Level Directory | Specify a directory or a list of directories under the source directory. If you leave this option blank, Enterprise Data Catalog imports all the files from the specified source directory. To specify a directory or a list of directories, you can perform the following steps: - 1. Click Select.... The Select First Level Directory dialog box appears.
- 2. Use one of the following options to select the required directories:
- - Select from list: select the required directories from a list of directories.
- - Select using regex: provide an SQL regular expression to select schemas that match the expression.
Note: If you want to select multiple directories, you must separate the directories with a semicolon (;). |
Recursive Scan | Recursively scans the subdirectories under the selected first-level directories. Recursive scan is required for partitioned file discovery. |
Enable Partitioned File Discovery | Identifies and publishes horizontally partitioned files under the same directory and files organized in hierarchical Hive-style directory structures as a single partitioned file. |
Case Sensitive | Specifies that the resource is configured for case sensitivity. Select one of the following values: - - True. Select this check box to specify that the resource is configured as case sensitive.
- - False. Clear this check box to specify that the resource is configured as case insensitive.
The default value is True. |
Memory | The memory required to run the scanner job. Select one of the following values based on the data set size imported: Note: For more information about the memory values, see the Tuning Enterprise Data Catalog Performance article on How To-Library Articles tab in the Informatica Doc Portal |
JVM Options | JVM parameters that you can set to configure scanner container. Use the following arguments to configure the parameters: - - -Dscannerloglevel=<DEBUG/INFO/ERROR>. Changes the log level of scanner to values, such as DEBUG, ERROR, or INFO. Default value is INFO.
- - -Dscanner.container.core=<No. of core>. Increases the core for the scanner container. The value should be a number.
- - -Dscanner.yarn.app.environment=<key=value>. Key pair value that you need to set in the Yarn environment. Use a comma to separate the key pair value.
- - -Dscanner.pmem.enabled.container.memory.jvm.memory.ratio=<1.0/2.0>. Increases the scanner container memory when pmem is enabled. Default value is 1.
- - -DmaxPartFilesToValidatePerTable=<number>. Validates the specified number of part files in the partitioned table. Default value is 10.
- - -DmaxPartFilesToValidatePerPartition=<number>. Validates the specified number of part files for each partition in the partition table. Default value is 5.
- - -DexcludePatterns=<comma separated regex patterns>. Excludes the files while parsing partition tables based on the regex pattern. By default, file names that start with a period and an underscore are excluded.
|
Track Data Source Changes | View metadata source change notifications in Enterprise Data Catalog. |
You can enable data discovery for an Azure Data Lake Store. For more information, see the
Enable Data Discovery topic. You can enable composite data domain discovery for an Azure Data Lake Store. For more information, see the
Composite Data Domain Discovery topic.