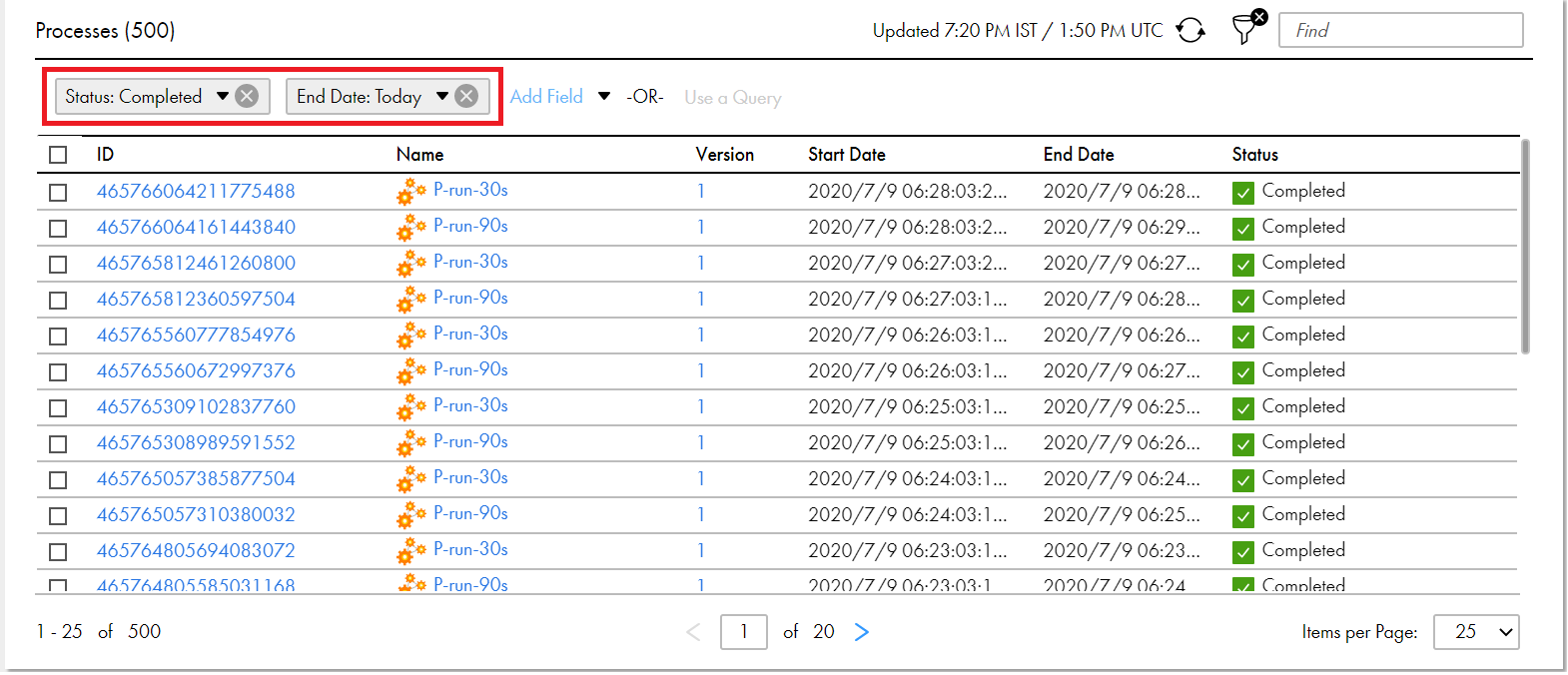

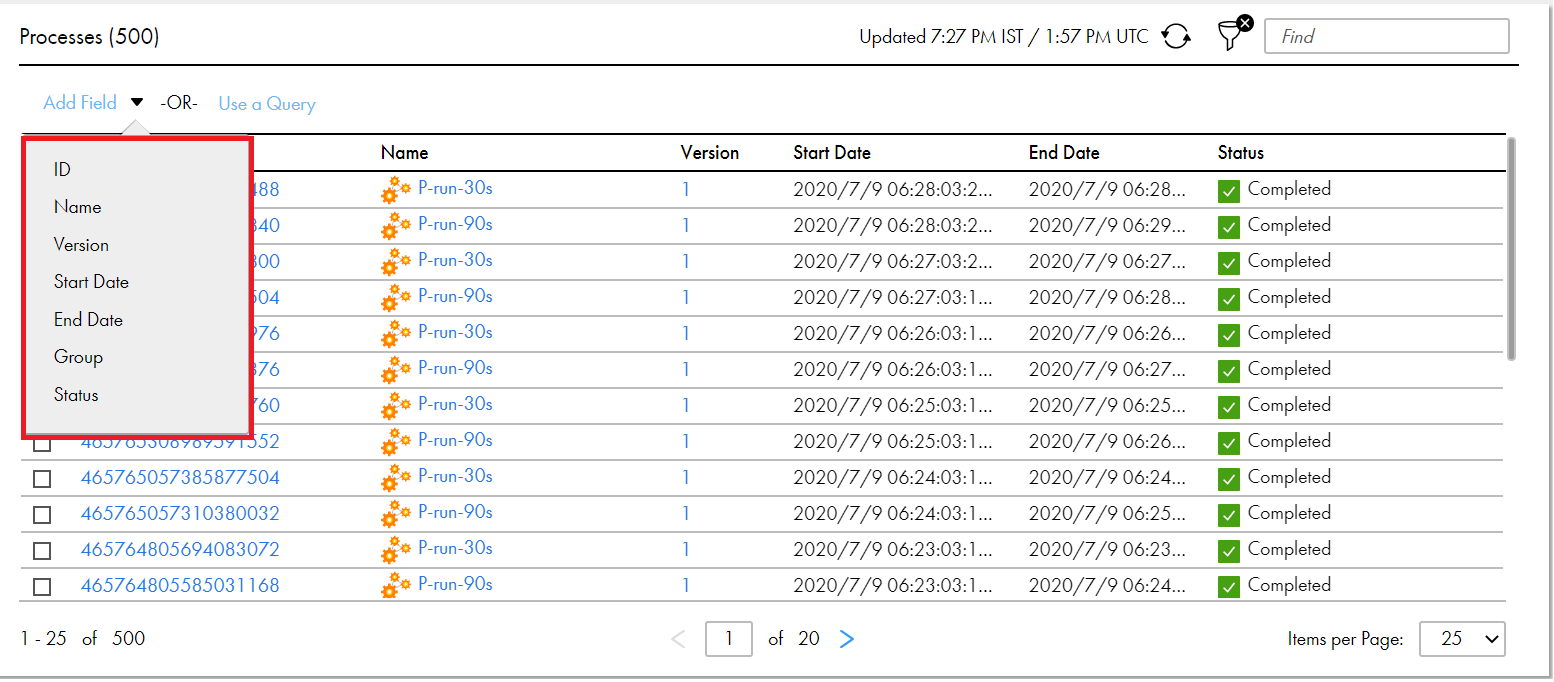
Field | Description |
|---|---|
ID | The instance ID of the process. Every process run has a unique instance ID. If you selected ID, complete the following steps:
If you selected the Between operator, enter two values to define a range based on which you want to filter the processes. |
Version | The version number of the process. If you selected Version, complete the following steps:
If you selected the Between operator, enter two values to define a range based on which you want to filter the processes. |
Name | The name of the process. If you selected Name, enter a value for the filter condition. |
Group | The group that a process belongs to. The group name is specified in the Process Deployment Descriptor (PDD) and displayed on the Deployed Process Version Detail page. If you selected Group, enter a value for the filter condition. |
Start Date | The date when the process execution started. If you selected Start Date, select one of the following values based on which you want to filter the processes:
If you selected Custom Range, click the calendar to specify a date and time range for the filter condition. |
End Date | The date when the process completed, faulted, or was stopped or suspended. If you selected End Date, select one of the following values based on which you want to filter the processes:
If you selected Custom Range, click the calendar to specify a date and time range for the filter condition. |
Status | The state of the process execution. If you selected Status, select one of the following values based on which you want to filter the processes:
|
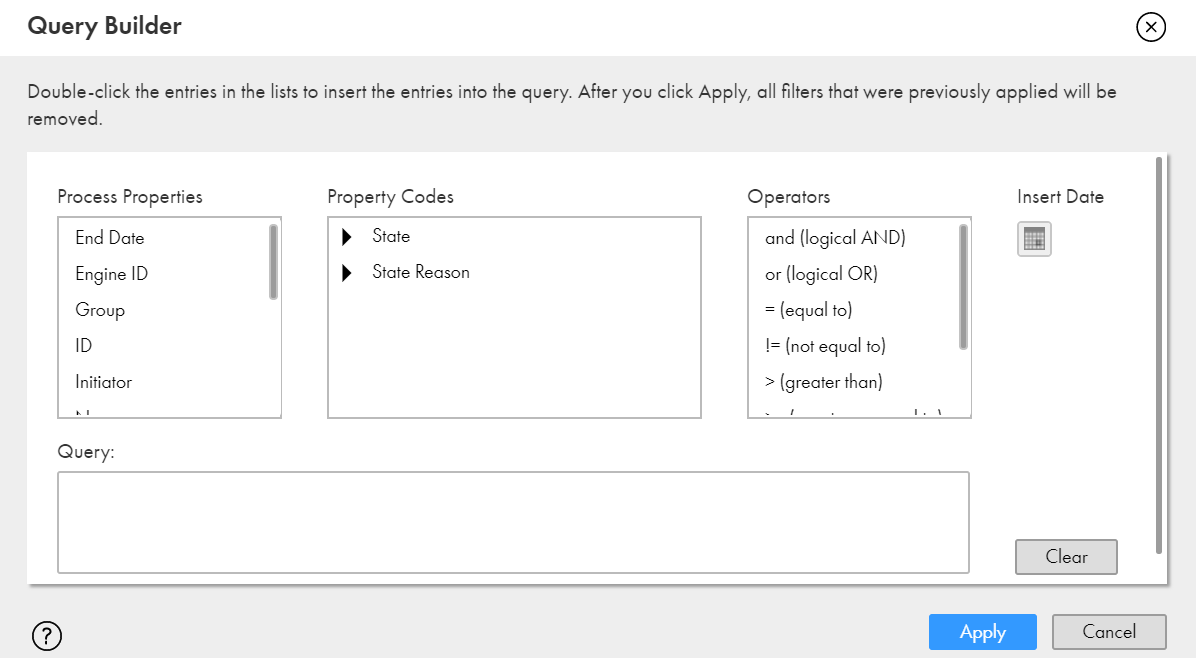
Process Property | Description | Sample Query |
|---|---|---|
End Date | The date when the process completed, faulted, or was stopped or suspended. The End Date field uses Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Double-click to add the getProcessProperty("EndDate") property to the query. Select an operator and click the calendar below the Insert Date field to select an end date. To use the = or != operator with an end date in the query, you must specify the end date in milliseconds. Otherwise, the query returns incorrect results. You can also use a range of dates in the query to filter processes based on the end date. | Use one of the following queries to filter the processes whose end date is August 21, 2020:
|
Engine ID | The ID of the engine that runs the process. Double-click to add the getProcessProperty("EngineId") property to the query. Select an operator and type a value for the engine ID. | Use the following query to filter the processes whose engine ID is 1: getProcessProperty("EngineId") = 1 |
Group | The group that a process belongs to. The group name is specified in the Process Deployment Descriptor (PDD) and displayed on the Deployed Process Version Detail page. Double-click to add the getProcessProperty("Group") property to the query. Select an operator and type a value for the group name. Enclose the group name within single quotation marks (') or double quotation marks ("). | Use the following query to filter the processes that belong to the North West Region group: getProcessProperty("Group") = "North West Region" |
ID | The instance ID of the process. Every process run has a unique instance ID. Double-click to add the getProcessProperty("Id") property to the query. Select an operator and type a value for the ID. | Use the following query to filter the processes whose instance ID is greater than 434251505437396992: getProcessProperty("Id") > 434251505437396992 |
Initiator | The name of the user who initiated the process. Double-click to add the getProcessProperty("Initiator") property to the query. Select an operator and type a name for the initiator. Enclose the initiator name within single quotation marks (') or double quotation marks ("). | Use the following query to filter the processes that were initiated by John: getProcessProperty("Initiator") = 'John' |
Name | The name of the process. Double-click to add the getProcessProperty("Name") property to the query. Select an operator and type a process name. Enclose the process name within single quotation marks (') or double quotation marks ("). | Use the following query to filter the processes whose name is LoanApproval: getProcessProperty("Name") = "LoanApproval" |
Namespace | The target namespace of the process. The target namespace uses the following syntax: urn:screenflow:process:<process_name> The target namespace value is unique for each process. Double-click to add the getProcessProperty("Namespace") property to the query. Select an operator and type a target namespace. Enclose the target namespace within single quotation marks (') or double quotation marks ("). | Use the following query to filter the process whose target namespace is urn:screenflow:process:LoanApproval: getProcessProperty("Namespace") = 'urn:screenflow:process:LoanApproval' |
Start Date | The date when the process execution started. The Start Date field uses Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Double-click to add the getProcessProperty("StartDate") property to the query. Select an operator and click the calendar below the Insert Date field to select a start date. To use the = or != operator with a start date in the query, you must specify the start date in milliseconds. Otherwise, the query returns incorrect results. You can also use a range of dates in the query to filter processes based on the start date. | Use one of the following queries to filter the processes whose start date is August 21, 2020:
|
State | The state of the process execution. Double-click to add the getProcessProperty("State") property to the query. Select an operator. In the Property Codes list, expand the State list and double-click a state value to insert the associated state code into the query. The following list describes the state values and the associated state codes:
| Use the following query to filter the processes that are in the faulted state: getProcessProperty("State") = "4" |
State Reason | The reason why a process is in the suspended state. Double-click to add the getProcessProperty("StateReason") property to the query. Select an operator. In the Property Codes list, expand the State Reason list and double-click a state reason value to insert the associated state reason code into the query. The following list describes the state reason values and the associated state reason codes:
| Use the following query to filter the processes that are in the suspended state because they faulted: getProcessProperty("StateReason") = 1 |
Tenant ID | The tenant identification number for the process. The tenant identification number is unique for each organization. Double-click to add the getProcessProperty("TenantId") property to the query. Select an operator and type a value for the tenant ID. Enclose the tenant ID within single quotation marks (') or double quotation marks ("). | Use the following query to filter the processes whose tenant ID is 3i5mW6m6816cHjNTPH8LwE: getProcessProperty("TenantId") = "3i5mW6m6816cHjNTPH8LwE" |
Title | The name of the process. Double-click to add the getProcessProperty("Title") property to the query. Select an operator and type a process name. Enclose the process name within single quotation marks (') or double quotation marks ("). | Use the following query to filter the processes whose name is LoanApproval: getProcessProperty("Name") = "LoanApproval" |
Version | The version number of the process. Double-click to add the getProcessProperty("Version") property to the query. Select an operator and type a value for the version number. | Use the following query to filter the processes whose version number is equal to 1: getProcessProperty("Version") = 1 |
Property Code | Description |
|---|---|
State | The state of the process execution. Expand the State list and double-click a state value to insert the associated state code into the query. The following list describes the state values and the associated state codes:
|
State Reason | The reason why a process is in the suspended state. Expand the State Reason list and double-click a state reason value to insert the associated state reason code into the query. The following list describes the state reason values and the associated state reason codes:
|
Operator | Description |
|---|---|
and | logical AND When you join two conditions with an and operator, the Process Server displays processes that meet both the conditions. For example, consider the following query: getProcessProperty("Name") = "C3" and getProcessProperty("Version") = 1 This query returns processes whose name is C3 and whose version number is 1 as shown in the following image: 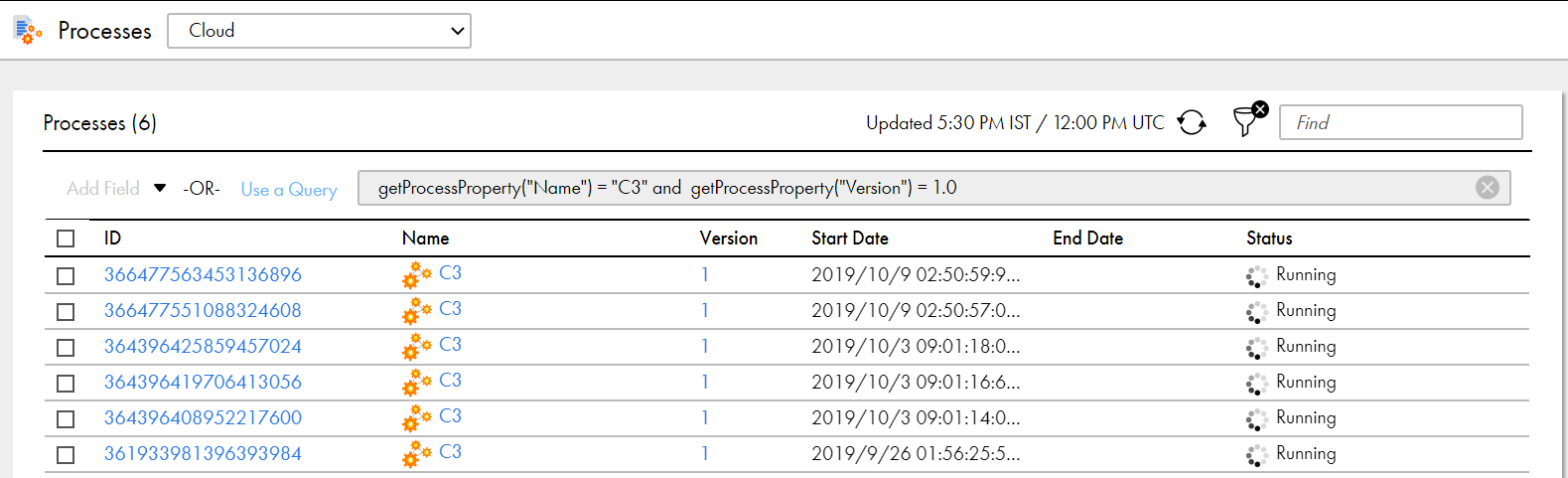 Note: The and operator is case sensitive. |
or | logical OR When you join two conditions with an or operator, the Process Server displays processes that meet either of the two conditions. For example, consider the following query: getProcessProperty("Name") = "C3" or getProcessProperty("Version") = 1 This query returns processes whose name is C3 as shown in the following image: 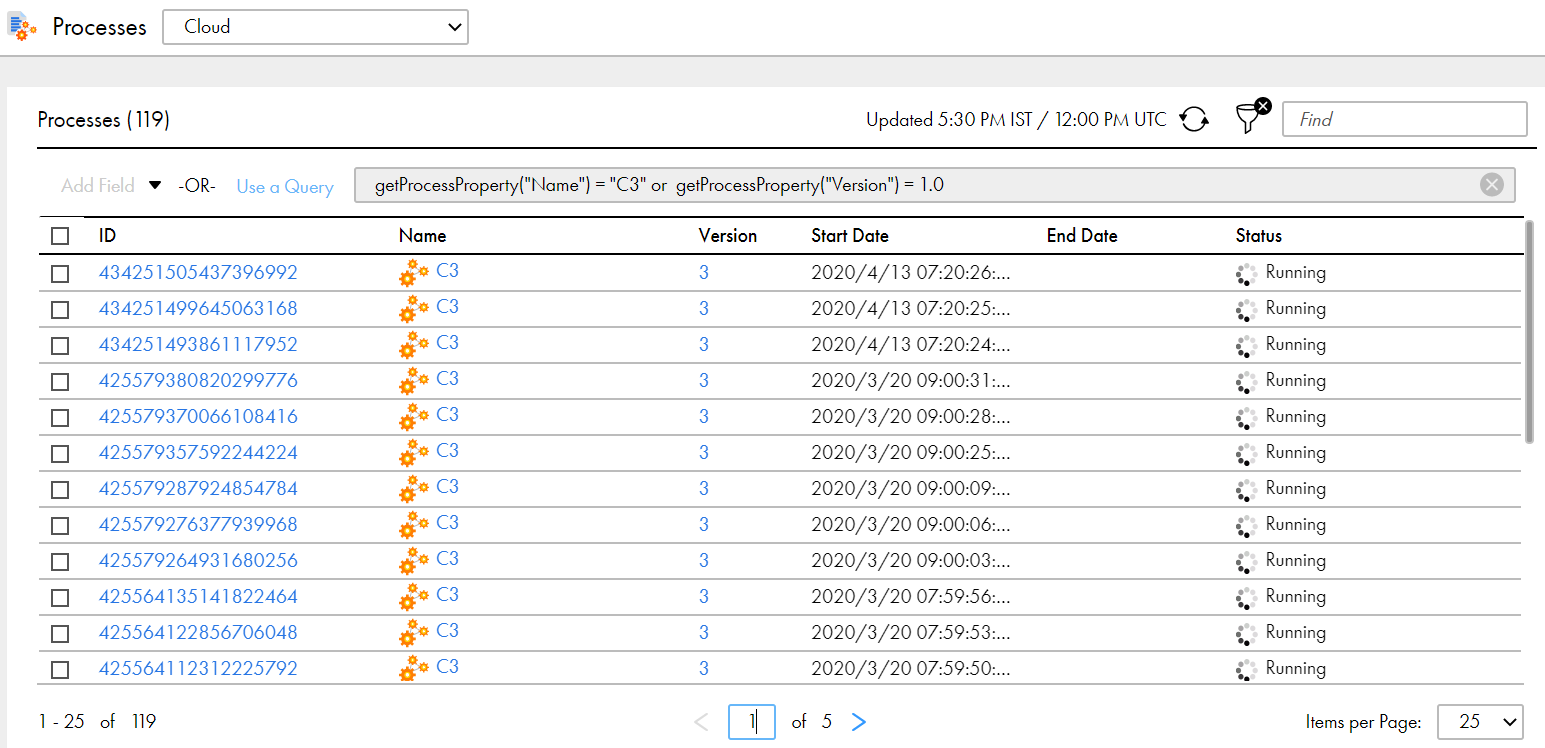 The query also returns processes whose version number is 1 as shown in the following image: 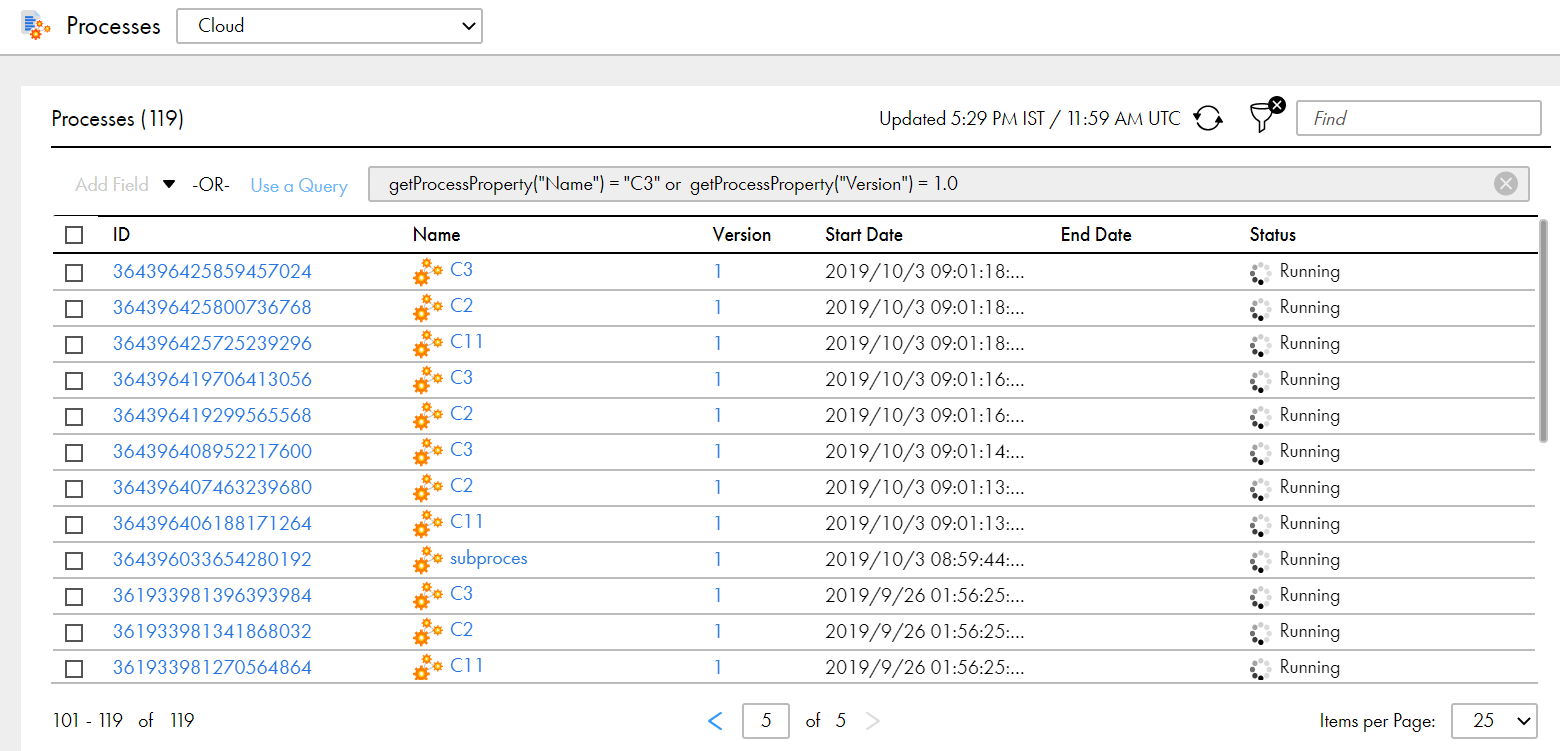 Note: The or operator is case sensitive. |
= | Equal to |
!= | Not equal to |
> | Greater than |
>= | Greater than or equal to |
< | Less than |
<= | Lesser than or equal to |
