Export - Substitute language
What is the substitute language? Where does it apply?
What is substitute language?
In the export, a substitute language can now be defined, so that if a value is not present in the requested language, that value is output in the defined substitute language. This functionality is available at main module level for fields that are qualified by a language, and in the submodules for attribute values, feature values, and file attachments.
The substitute language value specification is optional.
There's no special handling of the "language independent" language (key "-1").
How to configure substitute language
Global
There's no possibility to configure a substitute language on a global level.
Export template/ Export profile
You can define a language variable for an export format template and use it for substitute language configuration. If this variable is editable you can change its value in each export profile based on the export format template.
Data field
In the past, it was already possible to output the value of an alternative data field:
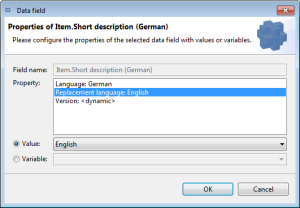
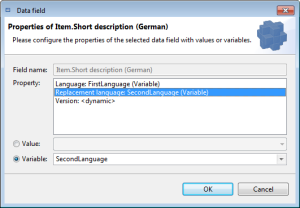
{?GetValue {&Item.Short description (German)}, {&Item.Short description (English)}}But now its much easier by using the substitute language. There's an additional "replacement language" logical key for each language-dependent data field. It's an optional key which can be configured with a language value corresponding to the language key of the data field, or with a variable representing a language.
Sub-module
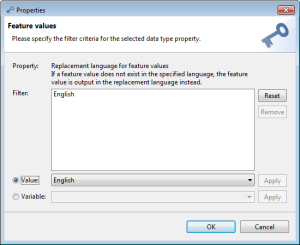
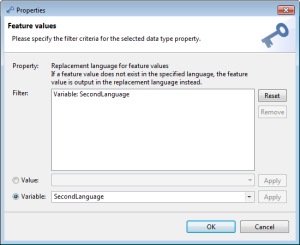
Some export sub-modules provide the new "Replacement language" data type filter. It's an optional, single value filter. A valid filter value is one of the language variables or languages supported by the corresponding "attribute value language" logical key:
Substitute language for data fields
Configuration
The export data field qualification dialog provides an additional "Replacement language" logical key for all language dependent data fields. A language dependent data field is a data field with a logical key that supports one of the language enumerations "Enum.Language" or "Enum.Language.WithLanguageIndependent".
You can define only one value for this "Replacement language" logical key, the default value is "<not selected>" which means there's no substitute language specified.
The following values can be used:
No value, the logical key has no value
One of the values provided by the enumeration of the "Language" logical key of the respective data field
One of the variables of the export data type "Language" that are assigned to the export template
A new variable that can be created in the data field qualification dialog directly by entering the new variable name
Data output
Without a substitute language
If there's no substitute language specified for a data field, the field value will be exported unchanged.
With a substitute language
When a substitute language has to be considered the following algorithm will be performed to get the value of a requested data field:
In addition to the data field, a substitute data field will be requested which is qualified identically to the data field except of the language
The value of the requested data field is not empty --> it's the value
The value of the requested data field is empty --> the value of the substitute field is used regardless of it's empty or not
There's no special handling of the "language independent" language (key "-1").
Customization
A customizing is not possible, the additional logical key is available for all language dependent data fields.
Substitute language for sub-modules
Configuration
The following export sub-data types provide an additional "Replacement language" data type filter:
Items
Item attribute values
Feature values
Item file attachments
Products
Product attribute values
Feature values
Product file attachments
Value list for defining product attributes (part of websphere integration feature)
Variants
Attribute values
Feature values
Variant file attachments
Structure groups:
Group feature values
Structure group file attachments
You can define only one value for this "Replacement language" data type filter, the default value is "<none>" which means there's no substitute language specified.
The following values can be used:
No value, the data type filter won't be used
One of the values provided by the enumeration of the "Language" logical key of the respective "attribute value" data field as configured in the repository. This could be another enumeration as of the "Language" logical key of the "attribute name" data field.
One of the variables of the export data type "Language" that are assigned to the export template
A new variable that can be created in the data type filter configuration dialog directly by entering the new variable name
Data output
"Language independent" language
There's no special handling of the "language independent" language (key "-1").
File attachment export
Export of file attachment data is described in "Understanding export functionalities". The corresponding sub-data types provide a "replacement language" data type filter, but the algorithm for building the output data differs.
Attribute values/ feature values export
Without substitute language
If there's no substitute language for attribute values specified the language specific attribute data will be merged with the attribute value data by their respective language only. The respective "Attribute language" repository entity is used as master entity, that means entries of the "Attribute value" repository entity will be omitted if there's no corresponding attribute language entry.
As a result, all exported entries contain identical languages in their language specific data and values.
Example:
|
Attribute 1 |
Attribute 2 |
|
|
Data |
Name de: Farbe Value de: rot |
Name de: Länge Value language independent: 42 |
|
Export |
Farbe (de): rot (de) |
Länge (de): |
With substitute language
As well as without a substitute language, the language specific attribute data will be merged with the attribute value data by their respective language only. The respective "Attribute language" repository entity is used as master entity, too. But in contrast to the case described above there's a value for the substitute language which will be used to find a corresponding substitute attribute value entry.
There're three cases to be considered:
There's no substitute attribute value entry
There's only a substitute attribute value entry
There're two matching entries: the original entry, and the substitute entry
Case 1 is identical to having no substitute language, it's described above.
If there's only the substitute value entry, it's taken to be merged with the respective language specific attribute entry. The "Attribute 2" example below refers to this case.
The algorithm for the 3rd case covers two situations:
If the attribute value is not empty the original entry will be used.
If the attribute value is empty the values of the "Attribute value", "Attribute value (max)", and "Language of attribute value" fields of the substitute entry will be used, all other values (sequence, reserve field values) of the original attribute value entry stay unchanged
Example:
|
Attribute 2 |
Attribute 3 |
Attribute 4 |
|
|
Data |
Name de: Länge Value language independent: 42 |
Name de: Besonderheit Value: keine Value en Value: <empty> Value language independent Value: - |
Name de: Toleranz Value de Value: 3 Value en Value: <empty> Value language independent Value: 0 |
|
Export Substitute language: language independent |
Länge (de): 42 (language independent), , 1 |
Besonderheit (de): keine (de), , 1 |
Toleranz (de): 3 (de), ,1 |
Customization
If you want to create a new export data type supporting the substitute language filter you need to implement the data type and a data provider that uses the configured substitute language to query the export data.
Data type
The DataType implementation overwrites the getDataTypeFilterGroups() method and adds the substitute language filter to the filter list:
@Override public DataTypeFilterGroup[] getDataTypeFilterGroups() { if ( this.dataTypeFilterGroups == null ) { // ... // substitute language Entity entity = RepositoryUtils.getRepositoryEntity( ENTITY_ARTICLE_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE ); String filterName = "Substitute language"; String filterDescription = "..."; DataTypeFilter substituteLanguageFilter = SubstituteLanguageDataTypeFilter.create( entity, filterName, filterDescription ); // ... List< DataTypeFilterGroup > filterGroups = new ArrayList< DataTypeFilterGroup >(); if ( substituteLanguageFilter != null ) { filterGroups.add( createAndRegisterDataTypeFilterGroup( substituteLanguageFilter ) ); } this.dataTypeFilterGroups = filterGroups.toArray( new DataTypeFilterGroup[0] ); } return this.dataTypeFilterGroups; }Data provider
The DataProvider implementation provides an appropriate queryData() method that analyzes and uses the configured substitute language value:
protected ListModel queryMySubListModel( DataType dataType, Pair[] fields, ExecutionContext executionContext ) throws CoreException{ Map< String, Object > additionalInfoMap = executionContext.getAdditionalInfoMap(); Long substituteLanguageId = SubstituteLanguageFilterSupport.getSubstituteLanguage( additionalInfoMap ); ListModel result = /* query the list model using substituteLanguageId */; result = postPrepareListModel( result, dataType, fields, executionContext ); return result;}Compatibility
Export format templates maintained with PIM 7 get a new version number. Older export format templates can be loaded, they will be converted into the newer version. The substitute language value of those export format templates is empty which is the default value.
Permissions
No special permissions are available.