In-Out Parameters
An in-out parameter is a placeholder for a value that stores a counter or task stage. Informatica Cloud evaluates the parameter at run time based on your configuration.
In-out parameters act as persistent task variables. The parameter values are updated during task execution. The parameter could store a date value for the last record loaded from a data warehouse or help you manage the update process for a slowly changing dimension table.
For example, you might use an in-out parameter in one of the following ways:
- •Update values after each task execution using a function in an Expression transformation: SetVariable, SetMaxVariable, SetMinVariable, or SetCountVariable. You can get updated values from the Activity Log after each task execution. You can get these values when you work in the Mapping Designer or through the REST API.
- • Handle incremental data loading for a data warehouse. In that case, you set a filter condition to select records from the source that meet the load criteria. When the task runs, you include an expression to increment the load process. You might choose to define the load process based on one of the following criteria:
- - A range of records configured in an expression to capture the maximum value of the record ID to process in a session.
- - A time interval, using parameters in an expression to capture the maximum date/time values, after which the session ends. You might want to evaluate and load transactions daily.
You can use in-out parameters in the following transformation types:
- •Source
- •Target
- •Aggregator (but not in expression macros)
- •Expression (but not in expression macros)
For each in-out parameter you configure the variable name, data type, default value, aggregation type, and retention policy. You can also use a parameter file that contains the value to be applied at run time. For a specific task run, you can change the value in the Mapping Configuration task.
Unlike input parameters, an in-out parameter can change each time a task runs. The Activity Log saves the latest value each time the task successfully runs. The next time the task runs, the Mapping Configuration task compares the in-out parameter to the saved value.
You can also reset the in-out parameters in a Mapping Configuration task, and then view the saved task values in the Activity Log.
Aggregation Types
The aggregation type of an in-out parameter determines the final current value of the parameter when the task runs. You can use variable functions with a corresponding aggregation type to set the parameter value at run time.
You can select one of the following aggregation types for each parameter:
Variable Functions
Variable functions determine how a task calculates the current value of an in-out parameter at run time.
You can use variable functions in an expression to set the current parameter value when a task runs.
To keep the parameter value consistent throughout the task run, use a valid aggregation type in the parameter definition. For example, you can use the SetMaxVariable function with the Max aggregation type but not the Min aggregation type.
The following table describes the available variable functions and the aggregation types and data types that you use with each function:
Variable Function | Description | Valid Aggregation Type | Valid Data Type |
|---|
SetVariable | Sets the parameter to the configured value. At the end of a task run, it compares the final current value to the start value. Based on the aggregation type, it saves a final value to the Activity Log. | Max or Min | All transformation data types |
SetMaxVariable | Sets the parameter to the maximum value of a group of values. | Max | All transformation data types |
SetMinVariable | Sets the parameter to the minimum value of a group of values. | Min | All transformation data types |
SetCountVariable | Increments the parameter value by one. | Count | Integer and bigint |
Note: Use variable functions one time for each in-out parameter in a pipeline. During run time, the task evaluates each function as it encounters the function in the mapping. As a result, the task might evaluate functions in a different order each time the task runs. This might cause inconsistent results if you use the same variable function multiple times in a mapping.
In-Out Parameter Properties
You can specify properties for each in-out parameter you define.
The following table describes the in-out parameter properties:
In-Out Parameter Property | Description |
|---|
Name | Required. Use the form: $$VariableName where VariableName is any alphanumeric or underscore characters. |
Description | Optional. Displays with the parameter name in the Activity Log and the Mapping Configuration task. |
Data Type | Required. Data type of the parameter. Note: Select a compatible aggregation type. For example, if you select string, you cannot configure it with the Count aggregation type. |
Precision | Required. Precision of the parameter. |
Scale | Optional. Scale of the parameter. |
Default Value | Optional. Default value for the parameter, which might be the initial value when the mapping first runs. Use any of the following formats for default values for datetime variables: - - MM/DD/YY
- - MM/DD/YY HH24:MI:SS
- - MM/DD/YYYY
- - MM/DD/YYYY HH24:MI:SS.US
|
Retention Policy | Required. Determines when the Mapping Configuration task retains the current value, based on the task completion status and the retention policy. Select one of the following options: - - On success or warning
- - On success
- - On warning
- - Never
|
Aggregation Type | Required. Aggregation type of the variable. Determines the type of calculation you can perform and the available variable functions. Select one of the following options: - - Count to count number of rows read from source.
- - Max to determine a maximum value from a group of values.
- - Min to determine a minimum value from a group of values.
|
In-Out Parameter Values
An in-out parameter is a placeholder for a value or values that the task applies at run time. You define the value of the in-out parameter in the mapping and you can edit the value when you configure the Mapping Configuration task.
A Mapping Configuration task uses the following values to evaluate the in-out parameter at run time:
- •Default Value. The value specified in the in-out parameter configuration.
- •Value. The current value of the parameter as the task progresses. When a task starts, the value is the same as the default value. As the task progresses, the task calculates the value using a function that you set for the parameter. The task evaluates the value as each row passes through the mapping. Unlike the default value, the value can change. The task saves the final value in the Activity Log after the task runs.
Note: If the task does not use a function to calculate the value of an in-out parameter, the task saves the default value of the parameter to the Activity Log as the initial current value.
At run time, the Mapping Configuration task looks for the value in one of these locations, in the following order:
- 1. Value in the parameter file
- 2. Value saved from the previous task run
- 3. Default value in the mapping
- 4. Default value for the data type
If you want to override a saved value, define a value for the in-out parameter in a parameter file. The task uses the value in the parameter file.
Rules and Guidelines for In-Out Parameters
Consider the following rules and guidelines:
- •When you write expressions that use in-out parameters, you do not need string identifiers for string variables.
- •When you use a parameter in a transformation, enclose string parameters in string identifiers, such as single quotation marks, to indicate the parameter is a string.
- •When required, change the format of a date/time parameter to match the format in the source.
- •If you copy a Mapping Configuration task, the session values of the in-out parameters are included.
- •If you import or export a Mapping Configuration task, the session values are not included.
- •You cannot use in-out parameters in a link rule or as part of a field name in a mapping.
- •You cannot use in-out parameters in an expression macro, as these rely on column names.
Creating an In-Out Parameter
You can configure an in-out parameter from the Mapping Designer.
- 1. In the Mapping Designer, add the transformation where you want to use an in-out parameter and add the upstream transformations.
- 2. Open the Parameters panel.
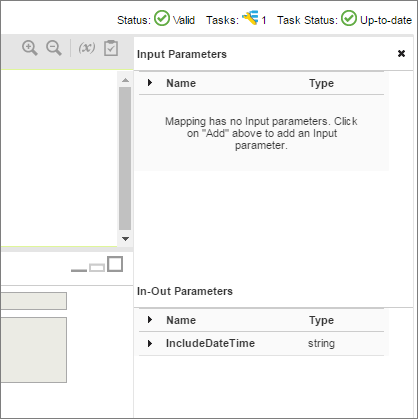
The In-Out Parameters display beneath the Input Parameters.
- 3. Add an in-out parameter.
- 4. Configure the parameter properties.
- 5. Use the parameter as a variable in the transformation where you want to set the value when the mapping runs.
For details on the in-out parameter properties and the Parameters panel, see
In-Out Parameter Properties and
Mapping Designer.
Editing In-Out Parameters in a Mapping Configuration Task
An in-out parameter is a placeholder for a value in a mapping. The task determines the value to apply during run time. You configure an in-out parameter in the mapping and can edit the value in the Mapping Configuration task.
When you deploy a mapping that includes an in-out parameter, the task sets the parameter value at run time based on the parameter's retention policy. By default, the Mapping Configuration task retains the value set during the last session. If needed, you can reset the value in the Mapping Configuration task.
From the Mapping Configuration task, you can perform the following actions for in-out parameters:
- •View the values of all in-out parameters in the mapping, which can change each time the task runs.
- •Reset the configuration to the default values. Click the Refresh icon to reset a single parameter. Click Refresh All to reset all the parameters.
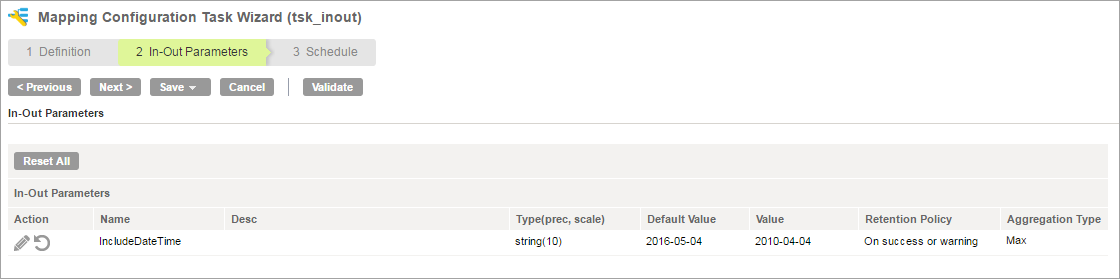
- •Edit or change specific configuration details. Click the Edit icon in the Action column.
For example, the following image shows configuration details of the IncludeDateTime parameter and the value at the end of the last session:
View In-Out Parameters in the Activity Log
The Activity Log displays the session variables output after a task runs. From the Activity Log, click the task name to open the job details.
The following image shows an example of the available details, including the current value of the specified parameter, set during the last session:
The In-Out Parameters from the Activity Log appear in the task instance based on the Retention Policy for each parameter.
In-Out Parameters Example
You can use an in-out parameter as a persistent task variable to manage an incremental data load.
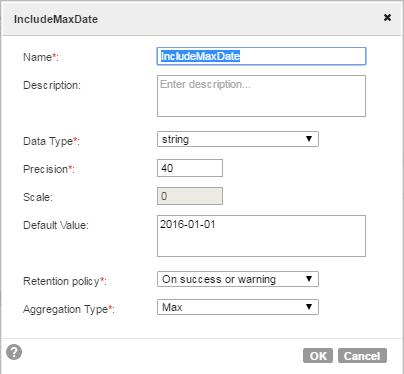
The following example uses an in-out parameter to set a date counter for the task and perform an incremental read of the source. Instead of manually entering a task override to filter source data each time the task runs, the mapping contains a parameter, $$IncludeMaxDate.
In the example shown here, the in-out parameter is a date field where you want to support the MM/DD/YYYY format. To support this format, you can use the SetVariable function in the expression transformation and a string data type.
Note: You can also configure a date/time data type if your source uses a date format like YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS. In that case, use the SetMaxVariable function.
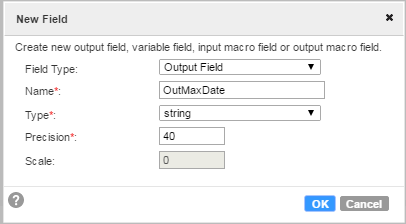
From the Mapping Design page, you open the parameters panel and configure an in-out parameter as shown in the following image:
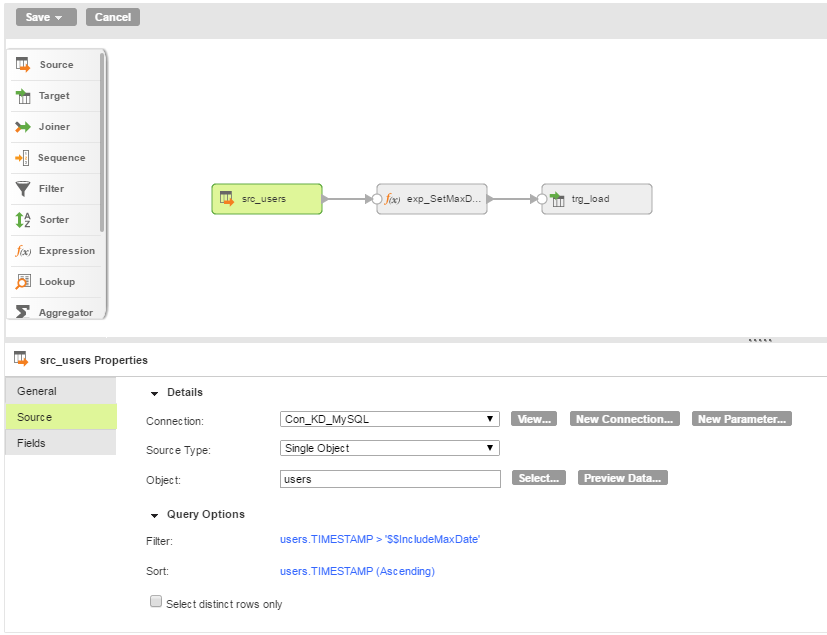
The sample mapping has the following transformations:
- •TheSource transformation applies the following filter to select rows from the users table where the transaction date, TIMESTAMP, is greater than the in-out parameter, $$IncludeMaxDate:
users.TIMESTAMP > '$$IncludeMaxDate'
The Source transformation also applies the following sort order to the output to simplify the expression in the next transformation:
users.TIMESTAMP (Ascending)
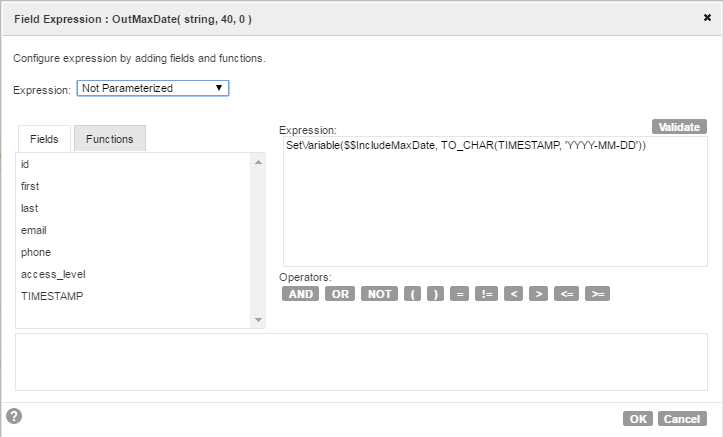
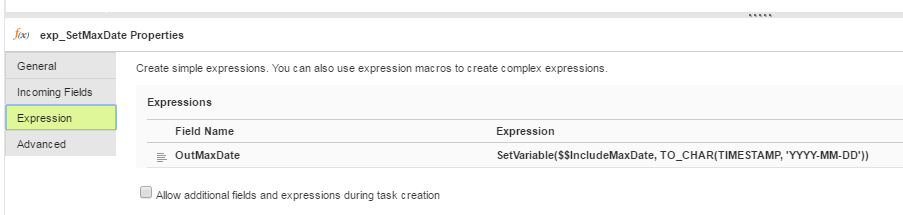
- •The Expression transformation contains a simple expression that sets the current value of $$IncludeMaxDate.
The Expression output field, OutMaxDate, is a string type that enables you to map the expression output to the target.
The SetVariable function sets the current parameter value each time the session runs. For example, if you set the default value of $$IncludeMaxDate to 2016-04-04, the task reads rows dated through 2016-04-04 the first time it runs. The task sets $$IncludeMaxDate to 2016-04-04 when the session is complete. The next time the session runs, the task reads rows with a date greater than 2016-04-04 based on the source filter.
You can view the saved expression for OutMaxDate, which also converts the source column to a DATE_ID in the format YYYY-MM-DD.
- •TheTarget transformation maps the Expression output field to a target column.
When the mapping runs, the OutMaxDate contains the last date for which the task loaded records.